Excellent software and practical tutorials
Introduction to Router Mode, Relay Mode and AP Mode
Wireless routers generally have AP (access point) mode, Router (wireless routing) mode, Repeater (relay) mode, Bridge (bridge) mode, and Client (client) mode.
Wireless routers provide a variety of working modes according to the needs of different user groups. Only by choosing the right mode can the router play its role to the fullest. The three common working modes of routers are:Routing Mode,Relay ModeandAP Mode, are there any differences between the different modes?

Routing Mode
Router mode is the most commonly used mode in our family life, and now it refers more to wireless routing mode.
Simply put, this mode allows the wireless router to connect to the optical modem to access the Internet. This mode accesses the Internet through the WAN port, can save broadband account passwords, IP addresses, gateways and other Internet information, and automatically dials to connect to the Internet.
After the router is successfully connected to the Internet, computers and mobile phones can access the Internet via wired or wireless connections to the router. In general, it allows multiple devices to share a network/broadband, which is often used in home environments.
In routing mode, the router is equivalent to an ordinary wireless broadband router; we usually use this mode. It needs to be connected to an ADSL Modem (cat) or optical modem for configuration.
Applicable places: Used when users have applied for broadband services themselves.
AP Mode
Plug an Internet cable into the router, and you can access the Internet through wired and wireless networks without any configuration; in this mode, you can access between wireless networks, wireless to wired networks, and wireless to wide area networks. In the final analysis, it is equivalent to a switch with wireless functions.
When the router is enabled in AP mode, it only acts as a wireless access point, with no distinction between WAN port and LAN port. Generally, when AP mode is enabled, the router is connected to the upper router via a network cable, converting the wired signal into a wireless signal to extend the wirelessNetwork Coveragescope.
It should be noted that the IP address obtained by the user device through the LAN port or wireless Internet access is the IP address assigned by the superior router, so this router cannot be managed.
Applicable occasions: For example, when it is only used as a wired and wireless access point and needs to communicate with the devices under the upper-level router.
Relay Mode
In Repeater mode, the router will establish a wireless connection with a wireless router that can access the Internet to amplify the wireless signal on the wireless router that can access the Internet.
The repeater mode can amplify the signal coverage of the existing WiFi network. With this mode, the wireless router can connect to the upper-level wireless network, thereby expanding the coverage of the WiFi network.
After the relay mode is set up, we can place the router at the edge of the original wireless signal to enhance the wireless signal. It is generally suitable for houses with complex layouts, large houses, etc.
Note: The name of the amplified wireless signal is the same as the wireless signal name of the original wireless router.
Applicable occasions: There is a wireless router that can access the Internet, but the wireless signal coverage of the wireless router is limited. It is used when you want the wireless signal to cover a wider range.
Bridge Mode
Bridge mode,The router will establish a wireless connection with a wireless router that can access the Internet to amplify the wireless signal on the wireless router that can access the Internet.;
Note: The name of the amplified wireless signal is different from the wireless signal name of the original wireless router.
Applicable occasions: There is a wireless router that can access the Internet, but the wireless signal of the wireless router covers a wired area, and you want the wireless signal to cover a wider range.
WDS Mode
WDS (Wireless Distribution System) is a protocol for wirelessly connecting two access points (AP). In the entire WDS wireless network, multiple APs are connected through bridges or repeaters, making the entire local area network mainly wireless.
The difference between repeater mode and bridge mode
Both Repeater mode and Bridge mode are wirelessly connected to a wireless router that can access the Internet, amplifying the wireless signal on the wireless router; the difference is that the name of the wireless signal after amplification in Repeater mode is the same as that on the previous router, while the name of the wireless signal after amplification in Bridge mode is different from the name of the wireless signal on the previous router.
The difference between repeater mode and AP mode
The most obvious difference is that the relay mode is connected to the upper router by "wireless" means, while the AP mode is connected to the upper router by "wired" means. In addition, the router in the relay mode can manage its own network (such as issuing IP addresses, etc.), while in the AP mode, the router is not responsible for managing the network, it is equivalent to a switch with wireless function, which converts wired signals into wireless signals.
What is the WDS function? What is the difference between bridge mode and repeater mode?
Generally, wireless routers can realize the above two modes, one is bridging and the other is relaying.
WDS bridging function:
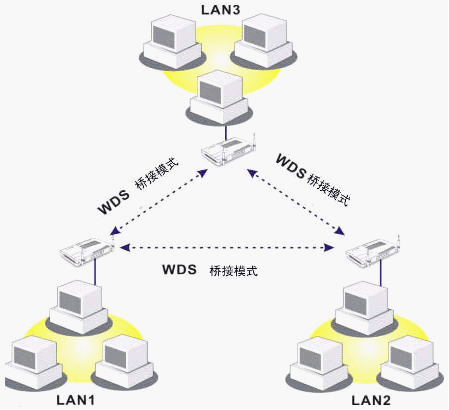
WDS relay function:
The main difference between the two modes is that in repeater mode, packets received from one access point can be forwarded to another access point via the WDS connection.
However, in bridge mode, packets received through the WDS connection can only be forwarded to the wired network or wireless hosts.
In other words, only the repeater mode can forward WDS to WDS packets.
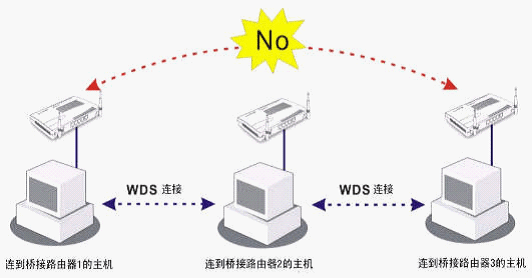
As shown in the figure below, the host connected to Bridge 1 or Bridge 3 can communicate with the host connected to Bridge 2 through the WDS link.
However, the host connected to Bridge1 cannot communicate with the host connected to Bridge3 through Bridge2.