Excellent software and practical tutorials
Ubuntu Netplan 50-cloud-init.yaml multi-IP configuration failure after reboot repair guide
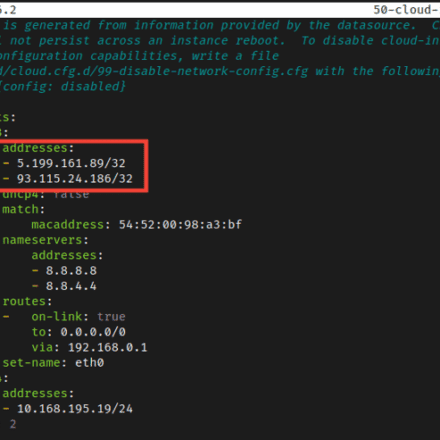
Your Netplan configuration (/etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml) rolls back to the original IP address after a reboot. This is usually caused by the cloud-init service resetting the network configuration on startup, or YAML syntax or permission issues that prevent the configuration from persisting. This is common in Ubuntu 20.04+, especially on cloud servers (such as Vultr and AWS). Don't worry, the fix is simple: check the syntax, disable cloud-init resets, and verify the application.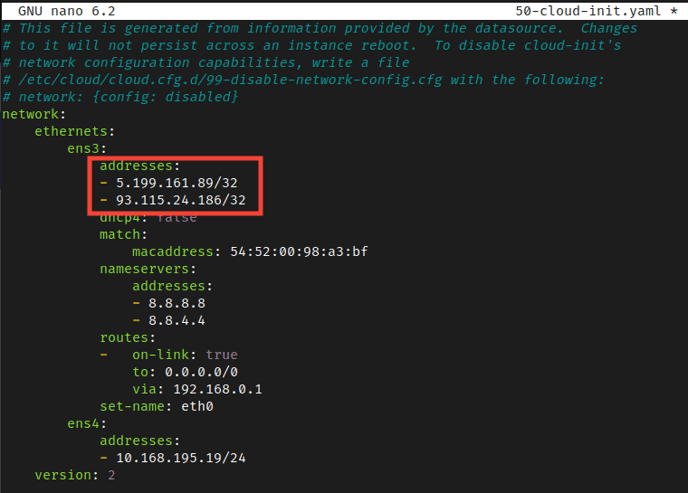
What is 50-cloud-init.yaml
This file is a key component of the Ubuntu Linux system directory 50-cloud-init.yaml. /etc/netplan/cloud-init This file defines the systemNetwork interfacenetwork configuration and setup, especially in cloud or virtualized environments.
Key features of 50-cloud-init.yaml:
Generated by cloud-init: This file is automatically generated by cloud-init, a tool designed to perform early initialization and customization of Linux systems, especially in cloud environments such as AWS, Azure, or virtualization platforms such as VMware.
Netplan Configuration: It uses the Netplan configuration system, which is Ubuntu's default system for defining network settings.
Not suitable for manual editing: This file typically contains comments indicating that changes made directly to it will not persist across reboots or reruns of cloud-init. This is because cloud-init can regenerate the file based on information provided by the data source.
Dynamic configuration: It typically configures the network interface using DHCP (for example, dhcp4: true) to automatically obtain an IP address, making it suitable for dynamic cloud environments.
Overriding: While direct editing is not recommended, you can override its settings by creating a new Netplan configuration file with a higher numerical prefix (e.g. 99-my-custom-config.yaml) in the /etc/netplan/ directory. This allows you to define static IP addresses or other specific network settings that take precedence.
Essentially, it serves as the initial network configuration provided by cloud-based or virtualized Ubuntu instances. While it is important to understand the system's default network settings, custom network configurations should be implemented in a separate Netplan file to ensure persistence.
Ubuntu 22.4 multi-IP configuration method
First, configure multiple IP addresses in 50-cloud-init.yaml
sudo vi /etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml
After configuration, save and exit :wq
Generate and test the configuration to check that the syntax is correct.
sudo netplan generate
If there is no problem, apply the configuration file.
sudo netplan apply
If an OVS warning appears after applying, please ignore it.
The following step is critical:
Disable cloud-init network reset, a critical step to prevent reboot rollback!
Create a new file
sudo vi /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/99-disable-network-config.cfg
Add it inside
network: {config: disabled}
Clear the cloud-init cache and instance ID
sudo cloud-init clean --logs sudo rm -rf /var/lib/cloud/instance # Delete instance data sudo dpkg-reconfigure cloud-init # Reconfigure, select "None" to disable the network module
Apply the configuration and test the restart
sudo netplan generate # to check syntax sudo netplan apply # to apply ip addr show # to verify multiple IP addresses immediately sudo reboot
If the above methods do not work, disable cloud-init completely (extreme case)
sudo touch /etc/cloud/cloud-init.disabled sudo systemctl disable cloud-init sudo systemctl mask cloud-init
Upgrade fix: Update cloud-init: sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade cloud-init (some versions have been fixed).
This solution is based on a community fix and generally works since 100%. If the issue persists after rebooting, leave a comment below with the output of cat /etc/netplan/*.yaml and journalctl -u cloud-init so I can help diagnose it!