Excellent software and practical tutorials
Some cloud hosts applied online have low memory. In order to meet the application requirements on the system, it is necessary to use a hard disk to increase the server's memory.Virtual MemoryHere's how to add virtual memory:SWAP.
What is swap
First of all, the concept of virtual memory is under Windows.linuxIt is also called swap partition.
Windows will use virtual memory even if the physical memory is not used up, but Linux will use virtual memory (i.e. swap partition) only when the physical memory is used up.
Swap is similar to the virtual memory of Windows, but the difference is that Windows can be set under any drive letter of Windows, and the default is C drive, and can be placed in the same partition as the system files. Linux, on the other hand, occupies an independent partition, which is convenient for putting part of the content in the swap partition when the memory demand is insufficient, and continue to execute when there is free memory, also called swap partition, and swap space is part of it.
The Windows virtual memory is automatically set by the computer, and the Linux swap partition is allocated when you install the system.
Create virtual memory swap
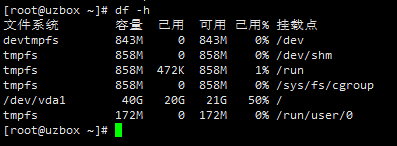
First, use the df command to view the space usage on the server.
The df command in Linux is used to check the disk space usage of the file system of the Linux server. You can use this command to obtain information such as how much space is occupied on the hard disk and how much space is currently left.
If the operating system does not configure swapfile (allocate swap space), it will cause errors after running for a period of time, and then start creating virtual memory, that is, the swap partition.
Check the memory configuration. If the number after Swap is 0, you need to add swap.
free -m
Create a file with preallocated space of the specified size:
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/swapfile bs=1024 count=8388608
You can check the file size using the ls command:
ls -lh /swapfile
Change the permissions of the swap file:
sudo chmod 600 /swapfile
Format the swap file:
sudo mkswap /swapfile
Enable the swap file:
sudo swapon /swapfile
Modify the fstab file to enable swap to take effect automatically after reboot:
sudo vi /etc/fstab
Add to the end of the file:
/swapfile swap swap sw 0 0
Or directly use the command to set the swap file to start at boot:
echo '/swapfile swap swap sw 0 0' | sudo tee -a /etc/fstab
If you want to stop swap:
swapoff /swapfile
If you want to delete swap:
rm -ir /swapfile
Finally, execute free -m to view the value after Swap.

The swap partition of 8G has been successfully created, and the Linux virtual memory has been created successfully.