Excellent software and practical tutorials

SEO Optimization
SEOoptimization Google SEOHow to do it? How different is it from Baidu SEO? In essence, there is not much difference, but there are some differences in details.Google SEOA few days ago, a friend from a large domestic e-commerce SEO department asked me a very interesting question.GoogleThe ranking issue cannot be explained in just one or two sentences, so I wrote a post to answer it, which may be helpful to other SEOs.
TDK Optimization
TDKtitle,description,keywordsA general term for the three. Of coursetitleis the most useful and is very worth optimizing;keywordsBecause it was overused by SEO people in the past, optimizing this now is useless for search engines, so I won’t go into it here;descriptionThe description will be directly displayed in the search introduction, so it is very effective for users to judge whether to click.
Title optimization
titleThe separators are usually,,_,-etc., among which_It is more friendly to Baidu,-It is more friendly to Google. The fourth character is a space. It can be used on English sites but rarely used on Chinese sites.titleThe length is generally about 30 Chinese characters on PC and 20 Chinese characters on mobile. If it exceeds this length, it will be truncated to ellipsis.
Because of business relations, we focus more on Baidu search engine optimization, so here are some suggestions for Baidu search engine optimization:
titleFormat:
- front page:
Website NameorWebsite name_Provide service introduction or product introduction - Channel Page:
Channel Name_Website Name - Article page:
Article title_channel name_website name
If your article title is not very long, you can also addKeywordsGo in, asArticle title_keywords_website name
Recommended Practice:
- Each web page should have a unique title. Avoid using the same default title for all pages.
- The title should be clear and contain the most important content of this web page.
- Be concise and don't list information that is irrelevant to the content of the webpage.
- Users usually browse from left to right, and important content should be placed at the front of the title.
- Use a language that users are familiar with. If you have both Chinese and English website names, try to use the one that users are familiar with as the title description.
Description optimization
descriptionIt is not a reference factor for weight calculation. The presence or absence of this tag does not affect the weight of the web page. It is only used as a selection target for search result summaries. Its length is about 78 Chinese characters on the PC side and 50 on the mobile side. If it exceeds, it will be truncated to an ellipsis.
Baidu recommends:
- Description is most suitable for website homepages, channel pages, product parameter pages, etc., which do not have long paragraphs of text that can be used as summaries.
- Describe the page accurately and don’t stuff keywords
- Create a different description for each page to avoid using the same description for all pages.
- Reasonable length, not too long or too short
Below are two examples recommended by Baidu for comparison. The first one does not apply meta description, while the second one does. It can be seen that the summary of the first result has basically no reference value to users, while the summary of the second result is more readable and can allow users to better understand the content of the website.

Page content optimization
Using HTML5 structure
If conditions permit (such as mobile terminals, compatible with IE9+, if IE8+, introduce it for IE8html5.jsIt's time to start considering using HTML5 semantic tags.header,footer,section,aside,nav,articleWait, here we take a screenshot to see the overall layout

Unique H1 title
Each page should have a unique h1 title, but not every page's h1 title is the site name. (However, in HTML5, the h1 title can appear multiple times, and each tag with a structural outline can have its own independent h1 title, such asheader,footer,section,aside,article)
The h1 title of the homepage is the site name, and the h1 title of the inner page is the title of each inner page. For example, the category page uses the category name, and the detail page uses the detail page title as the h1 title.
<!-- front page -->
<h1 class="page-tt">Tencent Classroom</h1>
<!-- Category Page -->
<h1 class="page-tt">Front-end development online training video tutorial</h1>
<!-- Details page -->
<h1 class="page-tt">html5+CSS3</h1>img settingsaltproperty
imgRequiredaltAttributes, if the width and height are fixed, please set the fixed values at the same time
<img src="" alt="seo优化实战" width="200" height="100" />nofollow
For links that do not need to be tracked and crawled, setnofollowIt can be used in blog comments, forum posts, social networking sites, message boards, etc. It can also be used for advertising links, privacy policies, user terms, logins, etc. The following code indicates that the link does not need to be tracked and crawled, which can prevent spiders from crawling and transferring weight.
<a href="http://example.com" rel="nofollow">no follow link</a>text
Content considerations:
- Nature Writing
- High-quality original content
- Writing techniques that attract readers
- Highlight selling points
- Enhance trust
- Lead to further behavior
User experience considerations:
- The layout is reasonable, clear, beautiful, and the fonts and background are easy to read
- The actual content is in the most important position of the page, and users can see it at a glance
- Substantial content and advertising can be clearly distinguished
- The first screen has substantial content, rather than requiring you to scroll down to see it
- The number of ads should not be too large, and their location should not hinder users from reading.
- If pictures and videos can help users understand the content of the page, try to create pictures and videos, etc.
- Avoid too many pop-ups
URL Optimization
URL design principles:
- The shorter the better
- Avoid too many parameters
- Keep directory levels as small as possible
- Use descriptive file and directory names
- Include keywords in the URL (except Chinese)
- All lowercase letters
- Use of hyphens
-Rather than_ - Directory format rather than file format
Static URL
With the current search engine crawling capabilities, it is not necessary to make the URL static, but in terms of ease of inclusion, user experience and social sharing, static and short URLs are more advantageous.
URL static or not?
Database-driven websites need to keep their URLs static, which has always been the most basic requirement for SEO and can be considered common sense. I'm afraid there are no websites that are not database-driven now.
In recent years, the SEO industry has unanimously agreed that having 2-3 question marks in a URL is not a problem, as search engines can usually index it, especially for domains with high authority, and having more question marks is not a problem. However, it is generally recommended to make the URL static anyway.
In September 2008, Google Webmaster Blog published a post discussing dynamic URLs vs. static URLs, which overturned this view. In this post, Google explicitly recommended not to make dynamic URLs static, but to keep the long dynamic URLs with question mark parameters. Google Blackboard and Chinese Webmaster Blog have translated and reposted it, and you can check it out.
Judging from the comments and blogs I've read, quite a few people actually think it makes sense and are prepared to do what Google says.
This is a relatively rare SEO suggestion from Google, and one that I strongly disagree with.
There are several key points in Google's post.
First, Google is fully capable of crawling dynamic URLs, and no matter how many question marks there are, it is not a problem. This is basically reliable. But what if there are more than ten or twenty question marks and parameters in the URL? How will Google view it? Even if it is capable of crawling, will it be willing to crawl it? How will other search engines deal with it?
Second, dynamic URLs are more helpful for Google spiders to understand the meaning of URLs and identify them, because the parameters in the URLs are suggestive. For example, Google gave this example:
http://www.example.com/article/bin/answer.foo?language=en&answer=3&sid=98971298178906&query=URL
The parameters in the URL help Google understand the URL and the content of the webpage. For example, the parameter after language is the prompt language, the parameter after answer is the article number, and the parameter after sid is definitely the session ID. Other commonly used parameters include the parameter after color refers to the color, the parameter after size refers to the size, etc. With the help of these parameters, Google can understand the webpage more easily.
When the URL is static, the meaning of these parameters usually becomes unclear. For example, this URL:
http://www.example.com/shoes/red/7/12/men/index.html
This could make it impossible for Google to tell which is the product serial number, which is the size, etc.
Third, it is easy to make mistakes when making a URL static, which is even more counterproductive. For example, if you change the order of parameters in a dynamic URL, the resulting page is actually the same. For example, these two URLs are likely to be the same page:
http://www.example.com/article/bin/answer.foo?language=en&answer=3
http://www.example.com/article/bin/answer.foo?answer=3&language=en
Keeping the dynamic URL makes it easier for Google to understand that it is the same web page. After the static URL is made, it is not easy for Google to determine whether the two URLs are the same page, which may cause duplicate content:
http://www.example.com/shoes/men/7/red/index.html
http://www.example.com/shoes/red/7/men/index.html
Another common mistake is the session ID, which can also be statically encoded in the URL:
http://www.example.com/article/bin/answer.foo/en/3/98971298178906/URL
This will generate a large number of pages with different URLs but the same content.
Therefore, Google recommends not to make URLs static.
But I still recommend staticization. The reasons are:
First of all, the advice given by Google is from Google itself, without considering other search engines. Just because Google has no problem crawling dynamic URLs does not mean that Yahoo, Baidu, Microsoft, etc. have no problem crawling dynamic URLs. Especially for Chinese websites, Google is not the boss. In fact, Baidu is still reluctant to crawl URLs with multiple question marks until now, in 2021.
Second, the disadvantages of staticization mentioned by Google are based on the assumption that staticization is done incorrectly. The problem is that if you want to do staticization, you have to do it correctly. It makes no sense to assume that it will be done incorrectly. How many people will put the session ID in when staticizing the URL?
Third, Google's suggestion is typically in its own favor, but not in the user's favor. URLs with question mark parameters may help Google understand the content, but they are obviously very difficult for users to understand the website structure and general content at a glance. Which of these two URLs is clearer, easier to read, and more likely to be clicked?
http://www.example.com/product/men/shoes/index.html
Obviously the second one.
Moreover, long dynamic URLs are not conducive to memory, and are not convenient for copying to others in emails, social networking sites, etc.
In short, although Google clearly recommends keeping dynamic URLs, I still recommend doing the opposite and making URLs static as much as possible.
URL Normalization
1. Unified connection
http://www.domainname.com
http://domainname.com
http://www.domainname.com/index.html
http://domainname.com/index.htmlThe above four are actually homepages. Although they will not cause any trouble to visitors, they are just four URLs with the same content to search engines, which may be mistaken as cheating. When search engines want to standardize URLs, they need to choose the best representative from these options, but the one they choose may not be what you want. So it is best to standardize it yourself.
2. 301 redirect
The first is when the URL changes. You must point the old address 301 to the new one, otherwise all the previous inclusion weighting will be in vain.
The second is somecmssystem, it is very likely that multiple paths will correspond to the same article.drupalThe default path isnode/nidHowever, if the path token is enabled, you can customize the path yourself. In this way, there are two paths corresponding to the same article. So you can enable 301 and finally redirect to one path.
3. canonical
This tag indicates the uniqueness of the page (this tag was not supported by Baidu before, but is supported now). It is used when passing parameters, such as:
//:ke.qq.com/download/app.html
//:ke.qq.com/download/app.html?from=123
//:ke.qq.com/download/app.html?from=456The above three represent three pages, but the last two are just to show where they come from, so in order to ensure that these three are the same page, weheadAddcanonicalLabel.
<link rel="cononical" href="//:ke.qq.com/download/download/app.html" />Robots
robots.txt
When a search engine spider visits a website, it will first visitRobots.txt file, robots.txt is used to instruct search engine spiders to prohibit crawling certain content of the website or only allow crawling of those contents, and is placed in the root directory of the site.
Take Tencent Classroom's robots.txt as an example:
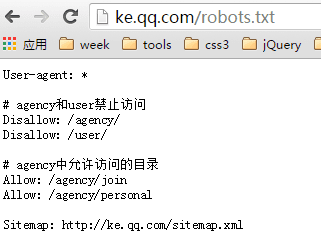
- User-agent indicates which spider the following rules apply to.
*Indicates all #Indicates comments- Disallow indicates that files or directories are prohibited from being crawled. Each line must be written separately.
- Allow indicates the files or directories that are allowed to be crawled. Each line must be written separately.
- Sitemap means site XML map, note the capital S
The following means that all search engine spiders are prohibited from crawling any content
User-agent: *
Disallow: /The following allows all search engine spiders to crawl any content
User-agent: *
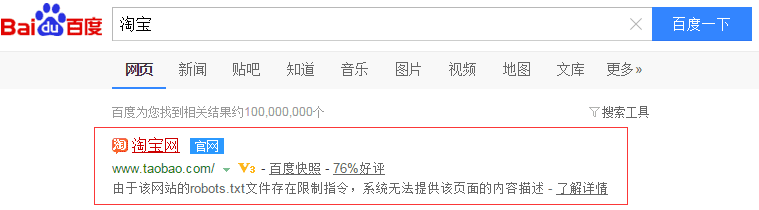
Disallow:Note: URLs that are prohibited from being crawled by robots can still be indexed and appear in search results. As long as there is an incoming link pointing to this URL, the search engine will know the existence of this URL. Although the page content will not be crawled, the index library still has information about this URL. Take Taobao as an example:
Prohibit Baidu search engine crawling
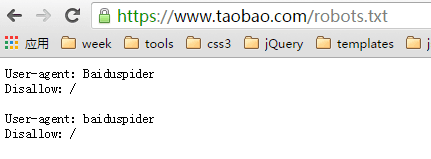
Baidu search shows
How to use robots.txt and its details
In China, website administrators do not seem to pay much attention to robots.txt. At the request of some friends, I would like to briefly talk about the writing of robots.txt through this article today.
Basic introduction to robots.txt
Robots.txt is a plain text file in which website administrators can declare parts of the website that they do not want to be accessed by robots, or specify that search engines only index specified content.
When a search robot (sometimes called a search spider) visits a site, it will first check whether there is a robots.txt in the root directory of the site. If it exists, the search robot will determine the scope of access according to the content of the file; if the file does not exist, the search robot will crawl along the link.
In addition, robots.txt must be placed in the root directory of a site, and the file name must be all lowercase.
Robots.txt writing syntax
First, let’s look at an example robots.txt: https://www.example.com/robots.txt
Visit the above specific address, we can see the specific content of robots.txt as follows:
# Robots.txt file from https://www.example.com
# All robots will spider the domain
User-agent: *
Disallow:
The above text means that all search robots are allowed to access all files under the https://uzbox.com site.
Specific syntax analysis: the text after # is explanatory information; User-agent: is followed by the name of the search robot. If it is followed by *, it refers to all search robots; Disallow: is followed by the file directory that is not allowed to access.
Below, I will list some specific uses of robots.txt:
Allow all robots to access
User-agent: *
Disallow:
Or you can create an empty file "/robots.txt" file
Block all search engines from accessing any part of the site
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
Block all search engines from accessing several sections of the site (directories 01, 02, and 03 in the example below)
User-agent: *
Disallow: /01/
Disallow: /02/
Disallow: /03/
Block access to a search engine (BadBot in the example below)
User-agent: BadBot
Disallow: /
Only allow access from a certain search engine (Crawler in the example below)
User-agent: Crawler
Disallow:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
In addition, I think it is necessary to expand on this and introduce robots meta:
The Robots META tag is mainly for specific pages. Like other META tags (such as the language used, page description, keywords, etc.), the Robots META tag is also placed in the <head> </head> of the page, specifically used to tell search engines how ROBOTS crawl the content of the page.
How to write the Robots META tag:
There is no case distinction in the Robots META tag. name="Robots" means all search engines, and can be written as name="BaiduSpider" for a specific search engine. contentThere are four command options in this section: index, noindex, follow, nofollow, and the commands are separated by ",".
The INDEX directive tells the search robot to crawl the page;
The FOLLOW instruction indicates that the search robot can continue crawling along the links on the page;
The default values for the Robots Meta tag are INDEX and FOLLOW, except for inktomi, for which the default value is INDEX, NOFOLLOW.
Thus, there are four combinations:
<META NAME="ROBOTS" CONTENT="INDEX,FOLLOW">
<META NAME="ROBOTS" CONTENT="NOINDEX,FOLLOW">
<META NAME="ROBOTS" CONTENT="INDEX,NOFOLLOW">
<META NAME="ROBOTS" CONTENT="NOINDEX,NOFOLLOW">
in
<META NAME="ROBOTS" CONTENT="INDEX,FOLLOW">can be written as <META NAME="ROBOTS" CONTENT="ALL">;
<META NAME="ROBOTS" CONTENT="NOINDEX,NOFOLLOW"> can be written as <META NAME="ROBOTS" CONTENT="NONE">
At present, it seems that most search engine robots comply with the rules of robots.txt. As for the Robots META tag, there are not many that support it, but it is gradually increasing. For example, the famous search engine GOOGLE fully supports it, and GOOGLE has also added a directive "archive", you can limit whether GOOGLE retains web page snapshots. For example:
<META NAME="googlebot" CONTENT="index,follow,noarchive">
It means crawling the pages in the site and following the links in the pages, but not keeping a snapshot of the page on GOOLGE.
How to use robots.txt
The robots.txt file restricts search engine robots (called bots) that crawl the web. These bots are automated and before they visit a web page they check to see if there is a robots.txt file that restricts them from visiting a specific page. If you want to protect certain content on your website from search engines, robots.txt is a simple and effective tool. Here's a quick guide on how to use it.
How to place a Robots.txt file
The robots.txt file itself is a text file. It must be located in the root directory of the domain and be named "robots.txt". A robots.txt file located in a subdirectory will not work because robots only look for this file in the root directory of the domain. For example, http://www.example.com/robots.txt is a valid location, but http://www.example.com/mysite/robots.txt is not.
Here is an example of robots.txt:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /cgi-bin/
Disallow: /tmp/
Disallow: /~name/
Use robots.txt files to block or remove entire sites
To remove your site from search engines and prevent all robots from crawling your site in the future, place the following robots.txt file in your server's root directory:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
To remove only your site from Google and prevent only Googlebot from crawling your site in the future, place the following robots.txt file in your server's root directory:
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: /
Each port should have its own robots.txt file. Especially if you host content over http and https, each protocol needs its own robots.txt file. For example, to have Googlebot index all http pages and not https pages, you would use the following robots.txt file.
For http protocol (http://www.example.com/robots.txt):
User-agent: *
Allow: /
For https protocol (https://www.example.com/robots.txt):
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
Allow all robots to access your pages
User-agent: *
Disallow:
(Alternative method: create an empty "/robots.txt" file, or do not use robots.txt.)
Block or remove pages using a robots.txt file
You can use a robots.txt file to block Googlebot from crawling pages on your site. For example, if you are manually creating a robots.txt file to block Googlebot from crawling all pages in a specific directory (for example, private), you could use the following robots.txt entry:
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: /private
To prevent Googlebot from crawling all files of a specific file type (for example, .gif), use the following robots.txt entry:
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: /*.gif$
To prevent Googlebot from crawling all URLs that contain ? (specifically, URLs that start with your domain name, followed by any string, followed by a question mark, followed by any string again), use the following entry:
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: /*?
Although we don't crawl or index the content of pages blocked by robots.txt, we may still crawl and index the URLs if we find them elsewhere on the web. As a result, the page URL and other publicly available information, such as anchor text in links pointing to the site, may appear in Google search results. However, the content on your page will not be crawled, indexed, or displayed.
As part of the Webmaster Tools, Google provides a robots.txt analysis tool. It can read the robots.txt file in the same way that Googlebot reads it, and can provide results for Google user-agents (such as Googlebot). We strongly recommend that you use it. Before creating a robots.txt file, it is necessary to consider what content can be searched by users and what should not be searched. In this way, by using robots.txt properly, search engines can bring users to your website while ensuring that private information is not included.
Myth 1: All files on my website need to be crawled by spiders, so there is no need to add a robots.txt file. If the file does not exist, all search spiders will be able to access all pages on the website that are not password protected by default.
Whenever a user tries to access a URL that doesn't exist, the server will log a 404 error (file not found). Whenever a search spider tries to find a robots.txt file that doesn't exist, the server will also log a 404 error, so you should add a robots.txt to your website.
Misconception 2: Setting all files in the robots.txt file to be crawled by search spiders can increase the inclusion rate of the website.
Even if the program scripts, style sheets and other files in the website are included by spiders, it will not increase the inclusion rate of the website, but will only waste server resources. Therefore, it is necessary to set in the robots.txt file not to let search spiders index these files.
The specific files that need to be excluded are introduced in detail in the article "Tips for using robots.txt".
Myth 3: Search spiders waste too much server resources to crawl web pages. The robots.txt file is set to prevent all search spiders from crawling all web pages.
If this happens, the entire website will not be indexed by search engines.
Tips for using robots.txt
1. Every time a user tries to access a URL that doesn't exist, the server will log a 404 error (file not found). Every time a search spider looks for a robots.txt file that doesn't exist, the server will also log a 404 error, so you should add a robots.txt to your website.
2. Webmasters must keep spider programs away from certain directories on the server to ensure server performance. For example, most web servers have programs stored in the "cgi-bin" directory, so it is a good idea to add "Disallow: /cgi-bin" in the robots.txt file to avoid all program files from being indexed by spiders, which can save server resources. Files that do not need to be crawled by spiders on general websites include: background management files, program scripts, attachments, database files, encoding files, style sheet files, template files, navigation images, background images, etc.
Below is the robots.txt file in VeryCMS:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /admin/ Backend management files
Disallow: /require/ program files
Disallow: /attachment/
Disallow: /images/ images
Disallow: /data/ database files
Disallow: /template/ Template files
Disallow: /css/ stylesheet files
Disallow: /lang/ encoded files
Disallow: /script/ script files
3. If your website has dynamic pages, and you have created static copies of these dynamic pages to make it easier for search spiders to crawl, then you need to set it in the robots.txt file to prevent dynamic pages from being indexed by spiders to ensure that these pages are not considered to contain duplicate content.
4. The robots.txt file can also directly include a link to the sitemap file. Like this:
Sitemap: sitemap.xml
The search engine companies that have expressed support for this include Google, Yahoo, Ask and MSN. Chinese search engine companies are obviously not in this circle. The advantage of this is that webmasters do not need to submit their sitemap files to each search engine's webmaster tools or similar webmaster sections. The search engine's spiders will crawl the robots.txt file, read the sitemap path in it, and then crawl the linked web pages.
5. Proper use of robots.txt files can also avoid errors during access. For example, you cannot allow searchers to directly enter the shopping cart page. Because there is no reason for the shopping cart to be included, you can set it in the robots.txt file to prevent searchers from directly entering the shopping cart page.
meta robots
If you want the URL not to appear in search results at all, you need to set meta robots
<meta name="robots" content="onindex,nofollow">The above code means: all search engines are prohibited from indexing this page and tracking the links on this page.
Of course there are other types of content, but each browser supports different types, so they are ignored here.
Sitemap
There are two formats for sitemaps: HTML and XML.
The HTML version is a normal HTML pagesitemap.html, users can directly access and list all the main links of the site. It is recommended that no more than 100 links should be listed.
The XML version of the sitemap was proposed by Google in 2005 and consists of XML tags, encoded asutf-8, lists all the URLs of the page. Its format is as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<url>
<loc>//ke.qq.com
<lastmod>2015-12-28</lastmod>
<changefreq>always</changefreq>
<priority>1.0</priority>
</url>
...
</urlset>inurlset,url,locThree are required tags.lastmod,changefreq,priorityIs an optional tag.
lastmodIndicates the time when the page was last updated.
changefreqIndicates the file update frequency, with the following values: always, hourly, daily, weekly, monthly, yearly, never. Always means that the content of the page is always changing, and the content is different every time the page is visited; never means that it never changes.
priorityIndicates the relative importance of the URL, the value range is0.0-1.0,1.0Indicates the most important, generally used on the homepage of the website, corresponding0.0The default importance is0.5(Note that the importance here is what we marked, which does not mean that the search engine will really rank according to the importance we set)
sitemap.xmlThe size of the sitemap file should not exceed 10M, and the number of URLs in each sitemap file should not exceed 50,000. When your sitemap file is very large, you can split it into multiple files. As shown below, there are two files, one for the basic page and one for the product details page.
<sitemapindex xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<Sitemap><loc>//ke.qq.com/sitemap-basic.xml2015-12-28T02:10Z
<Sitemap><loc>//ke.qq.com/sitemap-product.xml2015-12-28T02:10Z
</sitemapindex>SEO Tools
- Baidu Search Ranking
- Baidu Index
- Baidu Webmaster Platform
- meta seo inspector, check tag, google plugin
- seo in china, various data collected by Baidu, Google plug-in
- check my links, check links, google plugin
- seo quake, statistics of various data, Google plug-in
Finally, this article refers toBaidu SEO Guide 2.0 And Zac’s book “SEO Practical Code” (students who are interested in SEO can buy a copy and read it).