Excellent software and practical tutorials
Google Cloud Enable SSH service on Ubuntu
How to Ubuntu Enable SSH By default, when Ubuntu is initially installed, remote access via SSH is not allowed.Enabling SSH on Ubuntu Very simple and direct.
Follow the steps below as root or other sudo user to install and enable SSH on your Ubuntu system.

Configure SSH service
In the Google Cloud Platform virtual machine instance, click SSH and click Open in browser window.

After logging into the server, switch to administrator mode
sudo -i
Then set a root management password
passwd
 Update the system and then install openssh-server
Update the system and then install openssh-server
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y sudo apt install openssh-server
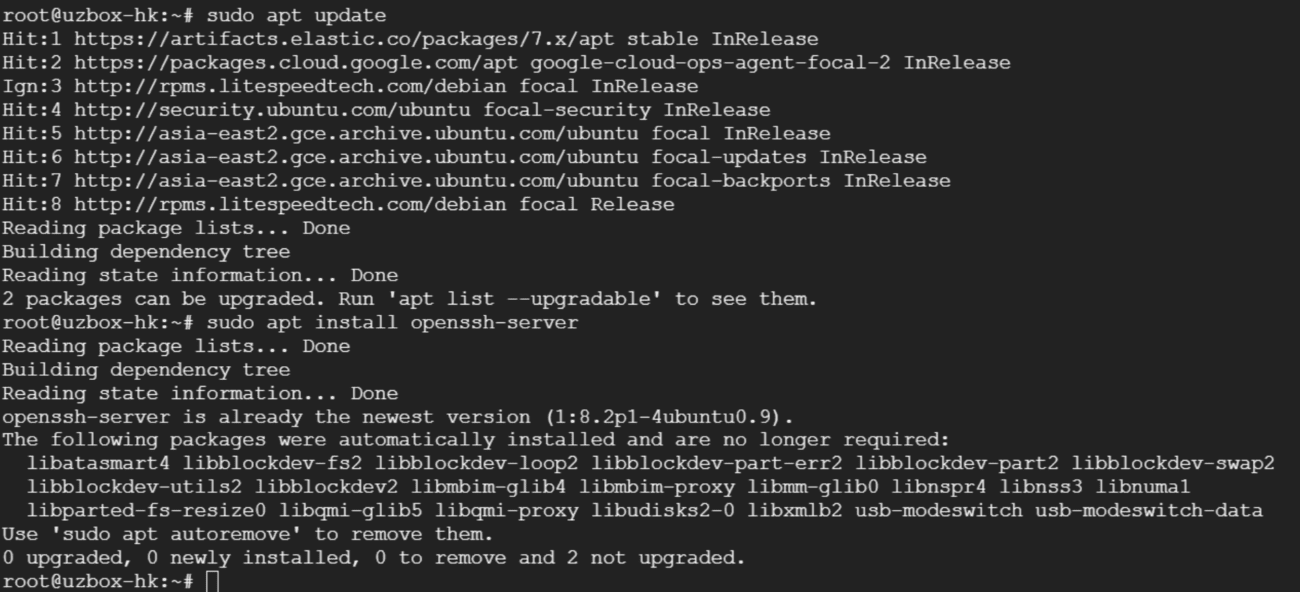 After the installation is complete, the SSH service will be automatically started. You can verify that SSH is running by typing:
After the installation is complete, the SSH service will be automatically started. You can verify that SSH is running by typing:
sudo systemctl status ssh
 Ubuntu comes with a built-in firewall configuration tool called UFW. If the firewall is enabled on your system, make sure the SSH port is open:
Ubuntu comes with a built-in firewall configuration tool called UFW. If the firewall is enabled on your system, make sure the SSH port is open:
sudo ufw allow ssh
enter sudo ufw status Press Enter to check the firewall status:inactive is closed,active It is turned on.
use sudo ufw enable Turn on the firewall.
use sudo ufw disable Turn off firewall
If UFW is not enabled, you can ignore this step. Ubuntu turns off the firewall by default. If you need to enable the firewall, use the above command to enable it.
LinuxThe default SSH port is 22. For security reasons, it is necessary to modify port 22 to 60000.
The modification method is as follows:
exist /etc/ssh/sshd_config Find Port 22 and change it to 60000.
If the user wants to open both ports 22 and 60000 at the same time, just /etc/ssh/sshd_config Just modify the parameters.
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Basic parameters:
- Port # port
- PermitRootLogin yes # allows root authentication login
- PasswordAuthentication yes # allows password authentication
By default, root login and password authentication are disabled. You need to change the value after the parameter to yes.
Just change the value after PermitRootLogin to yes.
 Then restart the ssh service
Then restart the ssh service
sudo systemctl restart ssh
Configuring swap partition
Linux swap partition (swap), or memory swap space, is an area on the disk, which can be a partition, a file, or a combination of them. The purpose of the swap partition is that when the system's physical memory is tight, Linux will save the infrequently accessed data in the memory to the swap, so that the system has more physical memory to serve each process, and when the system needs to access the content stored on the swap, the data on the swap is loaded into the memory, which is often called swap out and swap in.
Ubuntu checks the current swap partition size
 After installing CyberPanel in Ubuntu, the default Swap partition configured by CyberPanel is 2G, which is not enough at present. Let's see how to expand the Sawp partition.
After installing CyberPanel in Ubuntu, the default Swap partition configured by CyberPanel is 2G, which is not enough at present. Let's see how to expand the Sawp partition.
First check the swap partition mount location:
cat /proc/swaps
 Next, stop the default swap partition, delete the Swap partition, and then rebuild the Swap partition.
Next, stop the default swap partition, delete the Swap partition, and then rebuild the Swap partition.
#Stop Swap partitionsudo swapoff /cyberpanel.swap #After stopping, use free -m name to check whether Swap is successfully stopped free -m #swapon and swapoff commands are used to open or close swap space (including swap files and swap partitions) respectively #Delete swap partitionsudo rm /cyberpanel.swap
 Next, create a new Swap partition:
Next, create a new Swap partition:
#Create a 10G swap partitionsudo dd if=/dev/zero of=swapfile bs=1024 count=10000000 #Use the ll command to check whether the partition is created successfully #Set partition permissionssudo chmod 600 swapfile #Format the partitionsudo mkswap -f swapfile #Enable the partitionsudo swapon swapfile #Check the location of the new partitioncat /proc/swaps #Set the startup echo '/root/swapfile none swap sw 0 0' | sudo tee -a /etc/fstab
Permanently take effect on the swap partition.vi /etc/fstab Modify the /etc/fatab file and change /swapfile none swap sw 0 0 Add at the end.
Adjust kernel parameters:
Kernel parameters vm.swappiness controls the relative weight of swapping out runtime memory. The size of the parameter value has a great relationship with how the swap partition is used. The larger the value, the more actively the swap partition is used, and the smaller the value, the more actively the physical memory is used. The default value of the general system is swappiness=60, which means that the swap partition is used when the memory usage exceeds 100-60=40%. When swappiness=0, it means that the physical memory is used to the maximum extent, and then the swap space; when swappiness=100, it means that the swap partition is used actively and the data in the memory is moved to the swap space in time.
#Check the parameter value cat /proc/sys/vm/swappiness #If you want to temporarily adjust the parameter value, you can use the following command sysctl vm.swappiness = 50 #Permanently adjust the parameter value vi /etc/sysctl.conf #Modify the parameter vm.swappiness=50 in the /etc/sysctl.conf file #Or directly write echo "vm.swappiness = 80" >> /etc/sysctl.conf #Reload the parameter sysctl -p
 OpenCentOSBuilt-in TCP BBR Acceleration:
OpenCentOSBuilt-in TCP BBR Acceleration:
If the system kernel is higher than 4.9, BBR is included by default
Run the following code with root privileges, and the kernel version should be higher than 4.9.
uname -r
Enable BBR:
echo "net.core.default_qdisc = fq" >> /etc/sysctl.conf echo "net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control = bbr" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
Use the following command to make the modified BBR take effect:
sysctl -p
Execute the following command. If the result contains bbr, it proves that bbr is enabled in your kernel.
sysctl net.ipv4.tcp_available_congestion_control
Note: You can also execute the following command. If bbr is found in the result, it can also prove that bbr is enabled in your kernel.
lsmod | grep bbr
Or you can use BBRPLUS below
BBRplus Acceleration
The script includes three versions: BBR/BBR modified kernel, BBRplus kernel, and Lotserver (Sharp Speed) kernel.
wget -N --no-check-certificate "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/chiakge/Linux-NetSpeed/master/tcp.sh" && chmod +x tcp.sh && ./tcp.sh

Related Recommendations
How to mount a hard disk in Ubuntu and how to enable it after it is successfully mounted
Install WordPress with CyberPanel and configure pseudo-static rules









Very good