Excellent software and practical tutorials
Blockchain details the four levels of Web3 ecosystem architecture
Web3 So far, the ecosystem has taken shape. Web3 is the future of the Internet and the spring of blockchain. Let us take a closer look at what web3 is. If the current Web3 ecosystem is organized into a structural diagram, it can be divided into four levels from bottom to top:Blockchain network layer(Base layer),Middleware layer,Application Layer,Access Layer.
So what are the multiple layers for? Before we understand what Web3 is, let’s first understandWhat is blockchain!
What is blockchain
Blockchain (English: blockchain) is a peer-to-peer network system that uses cryptography and consensus mechanisms to create and store huge blocks of transaction data.
At present, the biggest application of blockchain technology is digital currency, such as the invention of Bitcoin. Because the essence of payment is "adding the amount reduced in account A to account B". If people have a public ledger that records all transactions of all accounts so far, then for any account, people can calculate the amount of money it currently has. The public blockchain is precisely the public ledger used to achieve this purpose. In the Bitcoin system, the Bitcoin address is equivalent to the account, and the number of Bitcoins is equivalent to the amount.
Each block contains the encrypted hash of the previous block, the corresponding timestamp, and the transaction data (usually represented by the hash value calculated by the Merkle tree algorithm). This design makes the block content difficult to tamper with. However, if you have the computing power of more than 51% of the blockchain node, you can manipulate the content of the blockchain. If the content written at the beginning is wrong, then the blockchain technology only makes it difficult to tamper with the wrong content.
Blockchain technology is an advanced database mechanism that allows transparent sharing of information across a corporate network. A blockchain database stores data in blocks, which are linked together into a chain. The data is consistent in time because you cannot delete or modify the chain without network consensus. Therefore, you can use blockchain technology to create an immutable ledger that allows you to track orders, payments, accounts, and other transactions.
What is Web3
Web3 (also known as Web 3.0, or web3) is a concept about the development of the global information network, mainly related to blockchain-based decentralization, cryptocurrency, and non-fungible tokens. The concept of web3 related to blockchain was proposed by Ethereum co-founder Gavin Wood in 2014, and has attracted the attention of cryptocurrency enthusiasts, large technology companies, and venture capital companies in 2021.
- Web3 is decentralized: rather than being controlled and owned by a centralized entity, most of the internet is distributed ownership between builders and users.
- Web3 is permissionless: everyone has equal access to participate in Web3, and no one is excluded.
- Web3 has native payment capabilities: it uses cryptocurrencies for online consumption and remittances, rather than relying on the outdated infrastructure of traditional banks or third-party payment institutions.
- Web3 is trustless: it works through incentives and economic mechanisms rather than relying on trusted third parties.
Web3 has become an all-encompassing term that represents a new and better vision for the Internet. At its core, Web3 is about returning power to users in the form of ownership through blockchain, cryptocurrency, and non-fungible tokens.
To sum it up in one simple sentence: Web1 is read-only, Web2 can read/write, and the future Web3 can read/write/own.
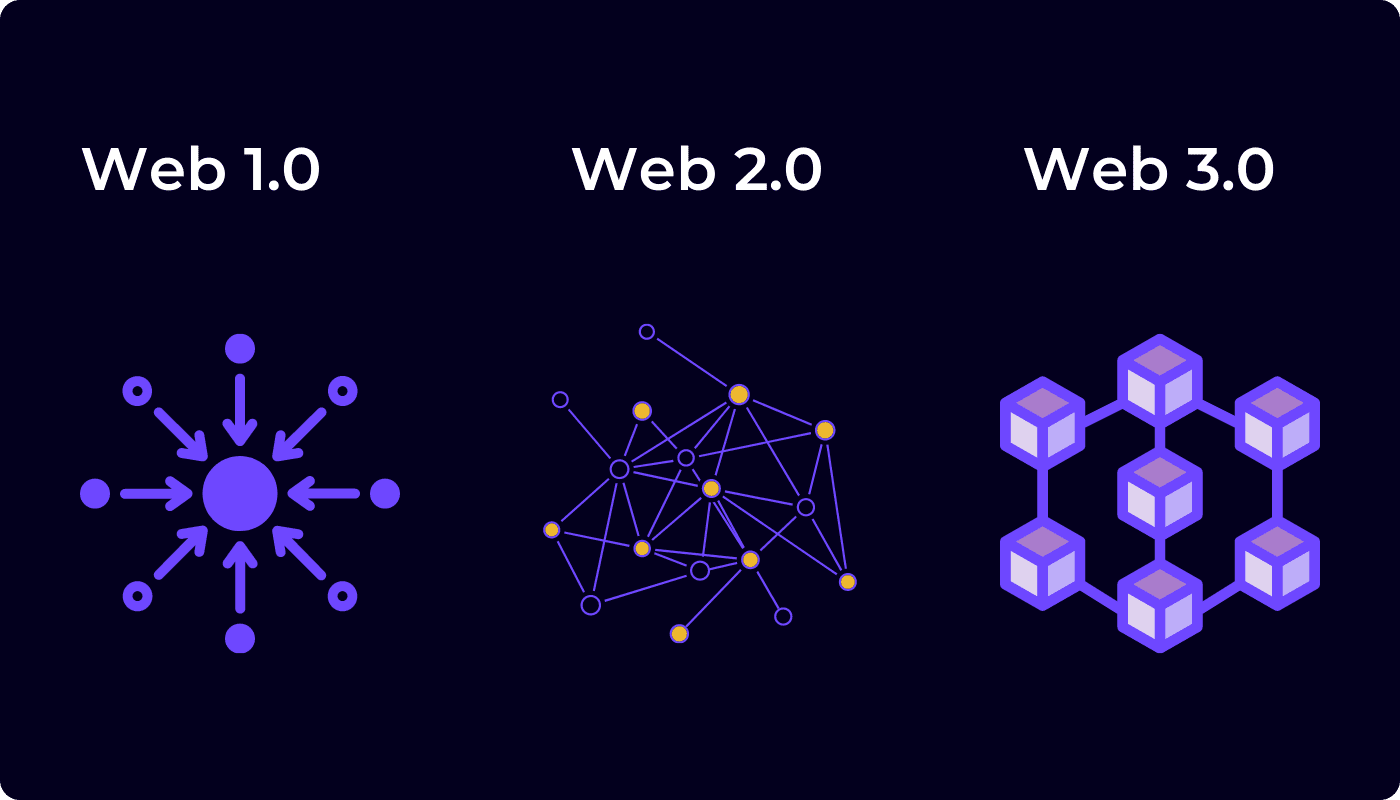
Next, let’s take a closer look at what each level of Web3 has.
Web3 blockchain network layer (base layer)
The bottom layer of Web3 is the blockchain network layer, also known as the basic layer. It is the cornerstone of Web3 and is mainly composed of various blockchain networks. The blockchain network mainly includes three modules: computing, storage, and network.
There are quite a few blockchain networks that make up this level, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, BNB Chain (BSC), Polygon, Arbitrum, Polkadot, Cosmos, Celestia, Avalanche, Aptos, Sui, and many more. According to Blockchain-Comparison, there are at least 150 blockchains as of the date of writing. Here we are mainly talking about public chains, not consortium chains. Because there are so many blockchains, it is a bit dazzling, so it is necessary to classify them.
First, there is a layered structure between different blockchains, including Layer 0, Layer 1, and Layer 2. Secondly, the prosperity and development of Web3 depends on smart contract technology, and the operating environment of smart contracts is a virtual machine.The relationship between smart contracts and virtual machines is similar to the relationship between Java programs and JVM. Blockchain can be divided into two categories based on different virtual machine dimensions: EVM chain and Non-EVM chain. EVM is the abbreviation of Ethereum Virtual Machine. EVM chain is a blockchain compatible with EVM, while Non-EVM is a blockchain incompatible with EVM. Finally, it can also be classified according to the size of the stored data, which can be divided into computing blockchain and storage blockchain.
Let’s start with the layered structure. The easiest to understand is Layer 1. Bitcoin, Ethereum, EOS, and BSC, which we are familiar with, all belong to Layer 1, also known as the main chain. In distributed systems, there is the CAP theorem, which means that a distributed system cannot simultaneously meet three characteristics: consistency, availability, and partition tolerance. A distributed system can only meet two of the three. The blockchain of Layer 1 is essentially a distributed system, and there is also the impossible triangle problem, but the three characteristics are different from CAP, namely: scalability, security, and decentralization. Each blockchain can only meet two of the three. Bitcoin and Ethereum tend to be secure and decentralized, so their scalability is relatively weak and their TPS is relatively low. EOS and BSC only rely on a few nodes to maintain consensus. Compared with Bitcoin and Ethereum, they reduce the decentralized characteristics but improve scalability, so that they can achieve a very high TPS.
In order to solve the scalability problem of Bitcoin and Ethereum, Layer2 was gradually derived. Layer2 exists as a subchain attached to the main chain, mainly used to carry the transaction volume of Layer1 and assume the role of the execution layer, while Layer1 can become a settlement layer, which can greatly reduce transaction pressure.At present, the mainstream Layer2s are all subchains that extend Ethereum, including Arbitrum, Optimism, zkSync, StarkNet, Polygon, etc. Bitcoin also has Layer2, mainly including Lightning Network, Stacks, RSK and Liquid, but they are relatively niche at present.
Layer 0 is more abstract and is generally defined as the blockchain infrastructure service layer, which is mainly composed of modular blockchains, including Celestia, Polkadot, Cosmos, etc. The concept of modular blockchain was mainly proposed by Celestia.The core design idea is to separate the consensus, execution, and data availability modules of the blockchain. Each module is completed by a separate chain, and then several modules are combined to complete the entire work.This is the same as the modular design concept advocated in software architecture design, which can achieve high cohesion and low coupling.
Cross-chain bridges or cross-chain protocols that implement cross-chain communication can also be classified as Layer 0. There are also a lot of cross-chain bridges. At the time of writing this article, there are as many as 113 cross-chain bridges counted on debridges.com. Among them, the three with the highest TVL rankings are the official cross-chain bridges of Polygon, Arbitrum, and Optimism. These bridges have realized cross-chain assets between their respective Layer 2 and Ethereum. The fourth in TVL is Multichain, formerly Anyswap, which is the third-party cross-chain bridge that connects the most blockchains. As of January this year, it has connected as many as 81 blockchains.
After discussing the division of the hierarchical structure, let’s sort out different blockchains from the perspective of EVM. As mentioned earlier, from the perspective of EVM, they can be divided into two categories: EVM chains and Non-EVM chains.
The EVM chain is currently the most mainstream direction, and the DApps and user groups based on the EVM chain are the largest in the entire Web3 ecosystem. Some are natively compatible with EVM, such as BSC, Heco, Arbitrum, Optimism, etc.; some are expanded to be compatible with EVM later, such as zkSync 1.0 is not compatible with EVM, while zkSync 2.0 is compatible with EVM. Even if many blockchains were not compatible with EVM in the early days, they are gradually embracing EVM. For example, Polkadot launched the Moonbeam parallel chain to be compatible with EVM, and Cosmos has Evmos.

At present, most of the top-ranked blockchains are already compatible with EVM, but there are still a few Non-EVM chains, such as Solana, Terra, NEAR, Aptos, and Sui. In addition, the smart contracts of EVM chains mainly use Solidity as the development language, while Non-EVM chains mainly use Rust or Move language to develop smart contracts.
The blockchains mentioned above are mainly blockchains that are used to solve decentralized computing problems. These blockchains generally do not support the storage of big data, such as file storage. Storage-type blockchains focus on solving the problem of big data storage. There are not many such blockchains at present, mainly Filecoin, Arweave, Storj, Siacoin and EthStorage.
The blockchain members that currently make up the "blockchain network layer" mainly include these. New members will continue to join in the future, but many old members will gradually decline and be left in the corner.
Web3 middleware layer
This layer above the blockchain network layer is what I callMiddleware layer. Mainly provided for upper layer applicationsVarious common services and functionsThe general services and functions provided include but are not limited to:Security audit, oracle, index query service, API service, data analysis, data storage, basic financial services, digital identity, DAO governanceetc. Components that provide common services and functions can be calledmiddlewareThese middlewares also exist in various forms, which can be on-chain protocols, off-chain platforms, or off-chain organizations, including centralized enterprises or decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). Let’s talk about the specific middlewares at this level.
Let's talk about security auditing first. This is a very core middleware. Because most of the blockchains and applications in Web3 are open source, and many are strongly related to finance, security has become a top priority, and security auditing has naturally become a rigid demand. Security auditing services are mostly provided by some security auditing companies. Well-known auditing companies include: CertiK, OpenZeppelin, ConsenSys, Hacken, Quantstamp, and domestic ones include SlowMist, ChainSec, and Paidun. In addition, there are many small auditing companies that are not well-known.
In addition to auditing companies, there are also some platforms that provide Bug Bounty. Generally, tasks are posted on these platforms to let white hat hackers find bugs. The higher the level of the bug security vulnerability found, the higher the bounty can be obtained. Currently, the world's largest Bug Bounty platform is Immunefi.
Next, let’s talk about Oracle Machine, which also plays a very important role in the Web3 ecosystem. It is a bridge between the blockchain system and external data sources, and mainly realizes the data intercommunication between smart contracts and the real world under the chain. Because the blockchain network itself has restrictions on state consistency, it is necessary to ensure that each node must obtain the same result given the same input. Therefore, the blockchain is designed as a closed system that can only obtain data within the chain, but cannot actively obtain data from external systems. However, external data is required in many application scenarios, and these external data are provided by oracles. This is also the only way for blockchain to achieve intercommunication with external data.
According to the specific functions provided by the oracle, the current classification of the oracle is roughly: DeFi oracle, NFT oracle, SocialFi oracle, cross-chain oracle, privacy oracle, credit oracle, decentralized oracle network. Specific oracle projects include CreDA, Privy, UMA, Banksea, DOS, NEST, Chainlink, etc. Among them, Chainlink is the leader of the oracle, which is positioned as a decentralized oracle network and has launched a series of products and services such as Data Feeds, VRF, Keepers, Proof of Reserve, CCIP, etc.
Then, the index query service is also a key middleware that solves the complex query problem of on-chain data. For example, if you want to query the total transaction volume on Uniswap on a certain day, it is very troublesome to query directly on the chain. Therefore, there is a demand for index query services, and the main representatives of this area are The Graph and Covalent. The implementation solution of The Graph is mainly to customize the monitoring of on-chain data and map it into custom data for storage, so as to facilitate query. Covalent encapsulates a lot of common and widely used data into a unified API service for users to query.
When it comes to API services, in addition to Covalent, there are also API providers that solve other different needs, such as: NFTScan, which focuses on providing NFT API data services; Infura and Alchemy, which mainly provide blockchain network node services; API3, which aims to create decentralized API services.
Whether it is index query service or API service, they are all services related to on-chain data. Data analysis is also a data-related service. The main members of this section include Dune Analytics, Flipside Crypto, DeBank, Chainalysis, etc.
The data storage middleware is easily confused with the underlying blockchains that specialize in storage. Some people also classify the underlying Filecoin, Arweave, Storj, etc. into this layer, but I think these are essentially underlying blockchains, so I classify them into the blockchain network layer. The data storage of the middleware layer is currently mainly IPFS. IPFS stands for InterPlanetary File System, and its Chinese name is InterPlanetary File System. It is a new hypermedia transmission protocol based on content addressing, distribution, and peer-to-peer, which aims to replace the HTTP protocol. IPFS is very similar to the blockchain network, but it does not actually belong to the blockchain network. Filecoin based on IPFS is the blockchain network.
Web3 Application Layer
The application layer is the most prosperous layer in the Web3 ecosystem. This layer is filled with various DApps, which can be described as a hundred flowers blooming and a hundred schools of thought contending. Below we mainly introduce several relatively prosperous sectors.
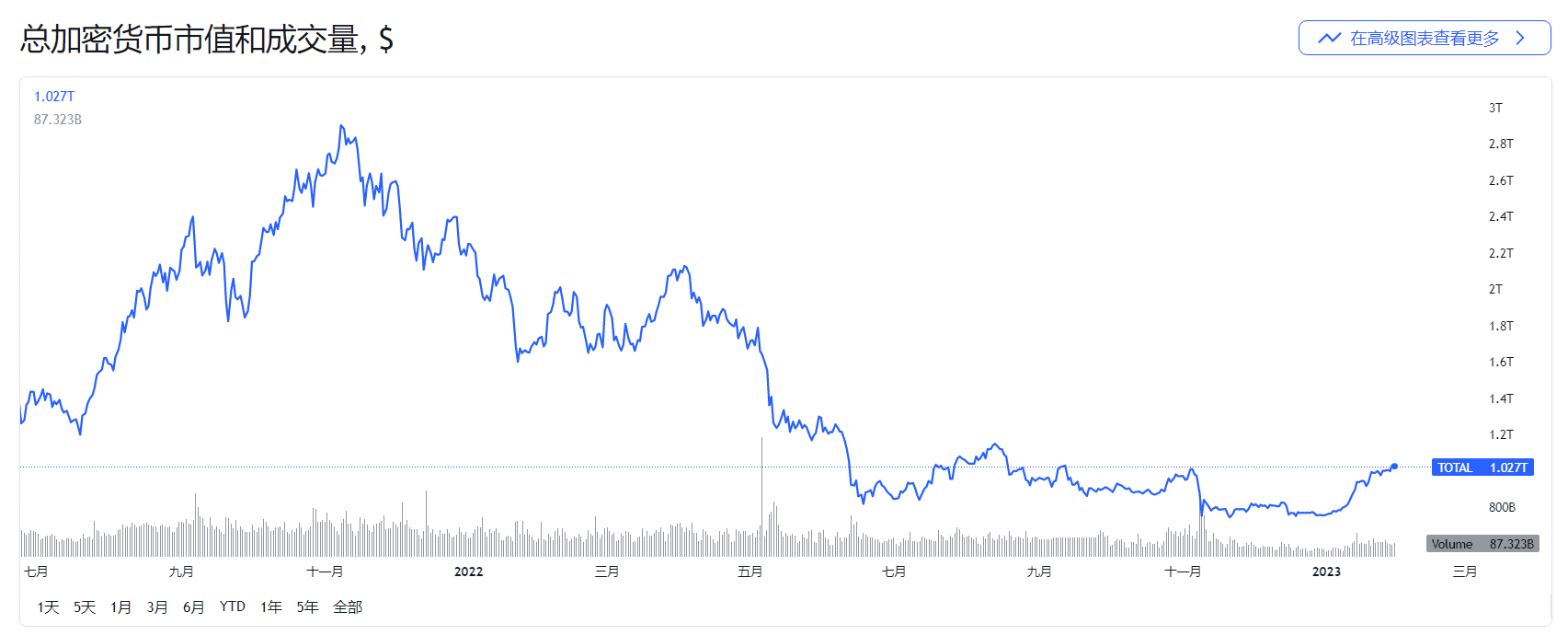
The above is the total market value of cryptocurrencies as of January 30, 2023.
Here are some websites that you can use to view real-time cryptocurrency data online.
- coinmarketcap:https://coinmarketcap.com/zh/
- crypto:https://crypto.com/price/zh-TW
- coingecko:https://www.coingecko.com/zh
NFT
The full name of NFT is Non-Fungible Token, which means "non-fungible token". It is also called digital collectibles in China and is used to represent unique digital assets such as artworks.
The first real NFT project is called CryptoPunks, which was released in June 2017 and consists of 10,000 24x24 pixel avatars. Each avatar is generated by an algorithm, unique, and all avatars are uploaded to Ethereum. It is also the only NFT project that has uploaded all avatar data to the chain. The following picture shows some avatars displayed on the CryptoPunks official website:
As of the date of writing, the floor price (i.e., the lowest price) of CryptoPunks is 66.88 ETH, which is approximately $84,397.21 when converted to US dollars based on the price of ETH. The most expensive CryptoPunk was sold for 8,000 ETH on February 12, 2022. It is difficult for many people to understand why an NFT avatar is so expensive. One of the main reasons is that it is the first NFT project, just like Bitcoin is the first blockchain, and its pioneering status brings great value potential.
Inspired by CryptoPunks, a company called Axiom Zen (the predecessor of Dapper Labs) released CryptoKitties at the end of November 2017. It is also known as CryptoKitties, Ethereum Cats, and CryptoKitties in China. After CryptoKitties went online, it spread like a virus, causing congestion on Ethereum and exposing Ethereum's performance problems. Before the release of CryptoKitties, Dieter Shirley, technical director of Axiom Zen, used CryptoKitties as an example and proposed the ERC721 Token protocol as a universal technical standard for NFTs. As CryptoKitties became popular, NFTs with ERC721 as the main technical standard were further adopted. Now ERC721 has become one of the basic standards for all NFTs.
After CryptoPunks and CryptoKitties, NFTs have gradually blossomed everywhere, and the NFT ecosystem has gradually flourished. NFTs have been involved in many fields since their development. If all the components of the NFT ecosystem are classified in detail, there can be as many as dozens of types. If we only focus on NFTs themselves, that is, the different use cases of NFTs, we can roughly make the following classifications:Collectibles, artwork, music, film, games, sports, virtual land, finance, brands, DIDThe following mainly introduces some representative NFT projects in each category.
 It is actually difficult to define collectibles as a category alone. Broadly speaking, almost anything can be classified as a collectible, including artworks, game props, virtual land, etc. NFTs that can be defined as collectibles must have one main characteristic: scarcity. For example, among 10,000 CryptoPunks, aliens have the least number, so they have high scarcity, while men have the most, so their scarcity is very low. The most well-known collectible NFTs, in addition to CryptoPunks, are BAYC, the full name of which is Bored Ape Yacht Club, also known as Bored Ape. Bored Ape is not just a separate set of NFTs, but actually just the beginning of the "Bored Ape Universe". Based on Bored Ape, the team behind it, Yuga Labs, has successively issued Bored Ape Kennel Club (BAKC), Mutant Ape Yacht Club (MAYC), and ApeCoin (APE) tokens, and launched Otherside, a virtual land specially built for the metaverse. All of these have formed the "Boring Ape Universe" series of IPs, and Boring Ape is not only popular in the crypto circle, but also has an increasing number of peripheral products outside the circle, such as Boring Ape hats, clothes, statues, restaurants, etc. Boring Ape's success has surpassed CryptoPunks, and Yuga Labs later directly acquired CryptoPunks.
It is actually difficult to define collectibles as a category alone. Broadly speaking, almost anything can be classified as a collectible, including artworks, game props, virtual land, etc. NFTs that can be defined as collectibles must have one main characteristic: scarcity. For example, among 10,000 CryptoPunks, aliens have the least number, so they have high scarcity, while men have the most, so their scarcity is very low. The most well-known collectible NFTs, in addition to CryptoPunks, are BAYC, the full name of which is Bored Ape Yacht Club, also known as Bored Ape. Bored Ape is not just a separate set of NFTs, but actually just the beginning of the "Bored Ape Universe". Based on Bored Ape, the team behind it, Yuga Labs, has successively issued Bored Ape Kennel Club (BAKC), Mutant Ape Yacht Club (MAYC), and ApeCoin (APE) tokens, and launched Otherside, a virtual land specially built for the metaverse. All of these have formed the "Boring Ape Universe" series of IPs, and Boring Ape is not only popular in the crypto circle, but also has an increasing number of peripheral products outside the circle, such as Boring Ape hats, clothes, statues, restaurants, etc. Boring Ape's success has surpassed CryptoPunks, and Yuga Labs later directly acquired CryptoPunks.
The characteristics of NFT can effectively protect the ownership of copyright, so it is natural that it has become popular in the field of art. There are several representative works of art NFT worth introducing. The first is the work of artist Beeple, called "EVERYDAYS: THE FIRST 5000 DAYS", which synthesizes all his works created one day in the past 5000 days (a total of 5000 works) into an NFT image, which was sold for US$69,346,250 in March 2021. The second one worth introducing is generative art, also known as derivative art. The artworks in generative art are not created by people, but automatically generated by programming algorithms. The most well-known NFT generative art platform is called Art Blocks, which is a randomly generated art platform based on Ethereum. Artists can upload their own unique algorithms to the Art Blocks platform and set a specific number of NFTs for issuance. NFTs will be automatically generated according to the algorithm. Finally, let me introduce the most expensive NFT artwork at present, called "The Merge", which was sold at a sky-high price of US$91.8 million in December 2021. Unlike other NFTs, "The Merge" is not a single work, but a dynamic combination of multiple "mass" tokens. What is actually sold is mass tokens. A total of 312,686 mass tokens were sold at the beginning, and there were 28,983 buyers. That is to say, "The Merge" is jointly owned by these 28,983 buyers, and the number of mass tokens owned by each buyer represents the share of ownership. "The Merge" can also be understood as a fragmented NFT work.
The rise of music NFTs is similar to that of artworks, mainly due to copyright. Here are a few representative music NFT-related figures. The first one to be introduced is Justin David Blau, an American DJ and electronic dance music producer, known by the stage name 3LAU. He was one of the first adopters of music NFTs and sold his first NFT in the fall of 2020. At the end of February 2021, the Ultraviolet NFT album brought him $11.68 million in revenue. In May 2021, the NFT music platform Royal was established, and in August it completed a seed round of financing of $16 million, with the participation of top institutions such as a16z and Coinbase. The second person to be introduced is Don Diablo, a Dutch DJ, digital artist, record producer, musician and electronic dance music creator, who sold his first complete concert film NFT in 2021, called "Destination Hexagonia", for 600 ETH (then $1.26 million). Finally, let me introduce a rock band called Kingship, a virtual band composed of bored apes and formed by Universal Music Group.
NFT has also swept the film and television industry. Several well-known film and television dramas have successively issued NFTs. Foreign ones include "Game of Thrones", "Batman", "The Lord of the Rings", "The Matrix", "The Walking Dead", etc., and domestic ones include "A Chinese Odyssey", "The Wandering Earth", "Dying to Survive", "Fengshen Trilogy", etc.
NFT is mainly used in games as a carrier of game assets. Compared with assets in traditional games, NFT allows game players to truly own game assets, and NFT can be circulated and traded outside the game. The first game NFT project is CryptoKitties, and each cat is an independent NFT. We will continue to talk about games in depth in the GameFi section later.
The sports field has also been involved in NFT. The two most well-known sports NFT platforms are NBA Top Shot and Sorare. NBA Top Shot, as the name suggests, is mainly based on the NBA, while Sorare serves the football field. In addition to the NBA and football, rugby, baseball, boxing, and wrestling have also launched their own NFT souvenirs.
Virtual land NFTs are mainly promoted by some projects that focus on the concept of "metaverse", the more well-known ones include Decentraland, The Sandbox, Roblox, Axie Infinity Land, Otherdeed, etc.
The combination of finance and NFT is mainly to apply NFT to DeFi, for example, the liquidity position in UniswapV3 is NFT. In addition, another idea is to fragment NFT first, and then give these fragmented NFTs DeFi functions, such as trading, lending, staking mining and other functions.
The combination of brands and NFTs is mainly a new marketing method. In the past two or three years, various brands have joined this camp, such as luxury brands such as GUCCI, LV, Hermes, catering brands such as Taco Bell, Starbucks, Pizza Hut, Coca-Cola, automobile brands such as McLaren, Chevrolet, sports brands such as Adidas, Li Ning, Nike, and many other brands.
Finally, let's talk about DID, which stands for Decentralized Identity. Everyone knows that DID is very important, but its development is still relatively slow. At present, except for the ENS domain name in the niche field, there is no mature DID system to form a network effect. At present, the most widely used is only the domain name, and ENS based on Ethereum is the leader. ENS is to Web3 what DNS is to Web2. The difference is that the domain name resolved by ENS is not mapped to the website IP, but to the user's Ethereum address. For example, the ENS of Ethereum founder Vitalik is "vitalik.eth", and the mapped address is 0xd8da6bf26964af9d7eed9e03e53415d37aa96045.
There are so many application scenarios for NFT that the categories listed above cannot cover all of them. Because of the characteristics of NFT, anything with ownership can be referred to, so there is a saying in the market that "everything can be NFT".
DeFi
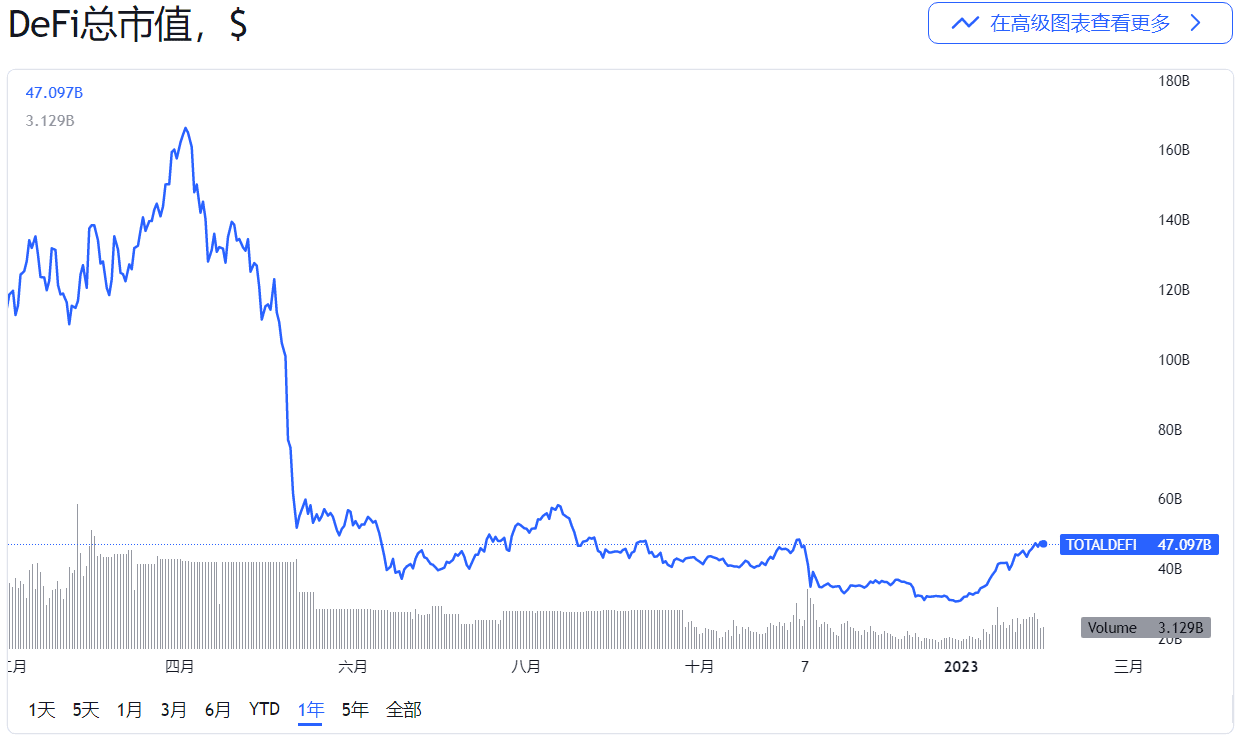
DeFi, or decentralized finance, emerged in the summer of 2020, so that period is also called DeFi Summer. According to statistics from TradingView, when DeFi first emerged in the summer of 2020, the total market value of DeFi was only US$5 billion, and then it soared all the way, reaching its peak at the end of 2021, nearly US$180 billion.
DeFi has many sub-sectors, mainly including:Stablecoins, exchanges, derivatives, lending, aggregators, insurance, prediction markets, indices, etc.
Stablecoins can be divided into three main categories:Centralized stablecoins, overcollateralized stablecoins, algorithmic stablecoinsAmong them, over-collateralized stablecoins and algorithmic stablecoins are decentralized stablecoins.
Centralized stablecoins are directly linked to legal tender and issued by centralized institutions, requiring each unit of stablecoin to have a 1:1 legal tender reserve. Currently, the two most traded stablecoins, USDT and USDC, are both legal tender-collateralized stablecoins, pegged 1:1 to the U.S. dollar, and issued by two centralized institutions, Tether and Circle, respectively. In addition, Binance, the world's largest centralized digital currency exchange, has jointly issued its own legal tender-collateralized stablecoin BUSD with Paxos, which is currently the third most traded stablecoin in the world, second only to USDT and USDC.
Overcollateralized stablecoins are forged by overcollateralizing other cryptocurrencies. The collateral will be locked in a smart contract, which will forge a corresponding number of stablecoins based on the value of the collateral. The smart contract relies on price oracles to maintain the peg with fiat currencies. This type of stablecoin is mainly represented by DAI, which was launched by MakerDAO and maintains a 1:1 peg with the US dollar. It currently ranks fourth in terms of trading volume.
Algorithmic stablecoins are relatively new. As the name suggests, they mainly control the supply of stablecoins through algorithms. There are many players in this field, including UST, FEI, AMPL, ESD, BAC, FRAX, CUSD, USDD, USDN, etc., but there is no truly stable algorithmic stablecoin yet.
Next, let's talk about exchanges. The exchanges in DeFi refer to decentralized exchanges, or DEXs for short. DEX is the sector with the highest market value among all DeFi sectors, and it is also the cornerstone sector of DeFi. If DEX is further subdivided, it can also be divided into spot DEX and derivatives DEX. Derivatives DEX mainly trades perpetual contracts or options. If divided by trading mode, DEX can be mainly divided into two types: Orderbook mode and AMM mode. DEXs in the Orderbook mode mainly include dYdX, apeX, 0x, Loopring, etc. There are more DEXs in the AMM mode, mainly including Uniswap, SushiSwap, PancakeSwap, Curve, Balancer, Bancor, GMX, Perpetual, etc.
The Orderbook model is the earliest type of transaction. The trading method is the same as the buying and selling method of the stock market. The trading user can choose to be a maker or a taker. The transaction will be matched according to the rules of price priority and time priority. DEX using Orderbook can be divided into three main models according to its development history:Pure on-chain matching + settlement model, off-chain matching + on-chain settlement model, Layer2 model.
In the pure on-chain matching and settlement model, the orders and takers submitted by users are directly on the chain, and the takers will be directly executed with the orders on the chain. The representative of this model is EtherDelta. Its advantages are that it is completely on-chain and highly decentralized, but its disadvantages are that the transaction performance is very low and the transaction cost is very high. Users need to pay fuel fees for placing and canceling orders.
The representative of the off-chain matching + on-chain settlement model is the 0x protocol. Compared with the first model, the main feature is the off-chain "relay" role. Users generate orders through off-chain signatures and submit them to the repeater, which maintains the Orderbook. The successfully matched orders are then submitted to the chain for settlement by the repeater. Because the matching is moved to the off-chain processing, the transaction performance is greatly improved, but the settlement is settled individually, so the settlement performance has become a bottleneck.
The representative of the Layer2 model is dYdX, and the technology behind it is mainly supported by StarkEx, a product provided by StarkWare. The basic principle is to deploy a separate, dedicated Layer2, where users' matching transactions and settlements occur, and then all transaction records (including settlement records) are packaged and proofs are generated and sent to Layer1 for verification. Unlike the Layer2 public chain, which provides general transactions, the Layer2 used by dYdX can only be used for dedicated trading scenarios. This is actually a private chain, which can also be called an application chain. This is also a new application model. The trading experience of this model is almost the same as that of a centralized exchange, but the degree of centralization is relatively high.
The current mainstream trading model that is completely decentralized and has a good trading experience is the AMM model. AMM is the abbreviation of Automated Market Maker, also known as the automatic market maker model. The AMM model was detonated by Uniswap, which was launched in November 2018. SushiSwap, PancakeSwap, Curve, etc. were all transformed based on the Uniswap model. This model requires a liquidity pool as support. The liquidity provider (LP for short) injects assets into the trading pool as liquidity, which is actually a capital pool. Then users trade directly with the liquidity pool, and LP earns transaction fees from users.
That’s all I have to say about exchanges for now. Let’s take a look at derivatives. The DeFi derivatives sector mainly includes several directions:Perpetual contracts, options, synthetic assets, interest rate derivatives.
Perpetual contracts are also futures contracts, leveraged trading products. The aforementioned dYdX, apeX, GMX, and Perpetual are several well-known perpetual contract DEXs. Options are more complicated than futures. The main players in the DeFi options field include Hegic, Charm, Opium, Primitive, Opyn, etc., but the current options market is still small and not much attention is paid. Synthetic assets are crypto assets that are tokenized by combining one or more assets/derivatives. In the early days, they mainly synthesized digital assets such as DAI and WBTC. Later, there were more and more synthetic assets based on stocks, currencies, precious metals, etc. in the real world. The current leading project in this track is Synthetix, and there are also projects such as Mirror, UMA, Linear, Duet, and Coinversation. DeFi's interest rate derivatives are mainly based on the development of different types of derivatives based on the interest rates of crypto assets to meet the different needs of DeFi users for deterministic returns. The main players are BarnBridge, Swivel Finance, Element Finance, etc.
Next, let's take a look at lending, which is also a high TVL sector. Like DEX, it is also the cornerstone of DeFi. The main lending protocols in this area are Compound, Aave, Maker, Cream, Liquity, Venus, Euler, Fuse, etc. At present, most lending protocols use an over-collateralized lending model. For example, if you want to borrow $80 worth of assets, you need to deposit at least $100 worth of collateral assets, that is, the value of the collateral assets must be higher than the value of the borrowed assets.
Although the overcollateralization model is the mainstream, there are also several innovative directions:Interest-free loans, asset isolation pools, cross-chain lending, credit loans. The representative of interest-free loans is Liquity. When users lend Liquity's stablecoin LUSD, users pay the borrowing and redemption fees in one lump sum, and no interest is required after lending. The asset isolation pool is to separate different lending assets into different pools. Each lending pool is independent to avoid the entire platform being affected by the damage of a bad asset or a pool. At present, asset isolation pools have almost become standard. Many lending protocols have introduced this model. In addition to Fuse, which has used this model from the beginning, protocols including Compound, Aave, and Euler have also joined the camp. Cross-chain lending is also a new trend. Flux, Compound, Aave, etc. are all expanding in this direction. Credit loans are very common in traditional finance, but they are still relatively rare in the DeFi field. The main reason is that there is still a lack of an effective on-chain credit system. The current representative project is Wing Finance.
The next one is the aggregator. DeFi aggregators are also divided into several types:DEX aggregator, yield aggregator, asset management aggregator, information aggregator. DEX aggregators mainly aggregate multiple DEXs together and find the optimal transaction path through algorithms. Mainstream DEX aggregators include 1inch, Matcha, ParaSwap, and MetaMask Swap built into the MetaMask wallet. Yield aggregators mainly include Yearn Finance, Alpha Finance, Harvest Finance, Convex Finance, etc. They mainly aggregate various liquidity mining to automate Yield Farming on multiple platforms. Asset management aggregators mainly monitor, track and manage the assets and liabilities of DeFi users, mainly represented by Zapper and Zerion. Finally, there are information aggregators, mainly including CoinMarketCap, DeFiPulse, DeBank, DeFiPrime and other platforms. In addition, these are actually centralized data platforms, but they still play an important role in the DeFi ecosystem. Not all applications in the DeFi ecosystem are decentralized.
Then, let's talk briefly about insurance. We know that insurance is a very large market in traditional finance, but the development of insurance in DeFi has been very slow so far. In the entire Web3 industry, there are many risks, such as protocol vulnerability risks, project runaway risks, regulatory risks, etc., so the market demand for DeFi insurance is actually very large, but because of the high threshold of development and design, and the relatively low liquidity, the entire insurance track has developed slowly. It is still in a very early stage. Nexus Mutual, Cover, Unslashed, Opium and other projects are the main players in this field.
Then, let’s look at the prediction market. The prediction market is a data-based market that can be used to bet on and predict all future events. It is also one of the earliest application scenarios in the Ethereum ecosystem and has experienced explosive growth in the 2020 US election. Major projects include PolyMarket, Augur, Omen, etc.
Finally, there is the index sector. Index funds that provide exposure to a basket of assets are gradually emerging in the DeFi field. But there are not many well-known indexes, mainly: DPI, sDEFI, PIPT, DEFI++. DPI is the full name of DeFi Pulse Index. It was created by DeFi Pulse and Set Protocol. It is a market value-weighted index that includes some mainstream DeFi protocol tokens as underlying assets, including Uniswap, Aave, Maker, Synthetix, Loopring, Compound, Sushi, etc. DPI can be redeemed for a basket of underlying assets. sDEFI is an index token launched by Synthetix and is the oldest index in the field. sDEFI is a synthetic asset that does not hold any underlying tokens, but uses oracle feeds to track token value. PIPT is the full name of Power Index Pool Token, which is issued by PowerPool and consists of 8 token assets. In addition to PIPT, PowerPool also issues three other indices: Yearn Lazy Ape Index, Yearn Ecosystem Token Index, and ASSY Index. DEFI++ is issued by PieDAO, which consists of 14 assets. PieDAO also issued BCP and PLAY. BCP consists of three tokens: WBTC, WETH, and DEFI++, while PLAY consists of tokens of some metaverse projects.
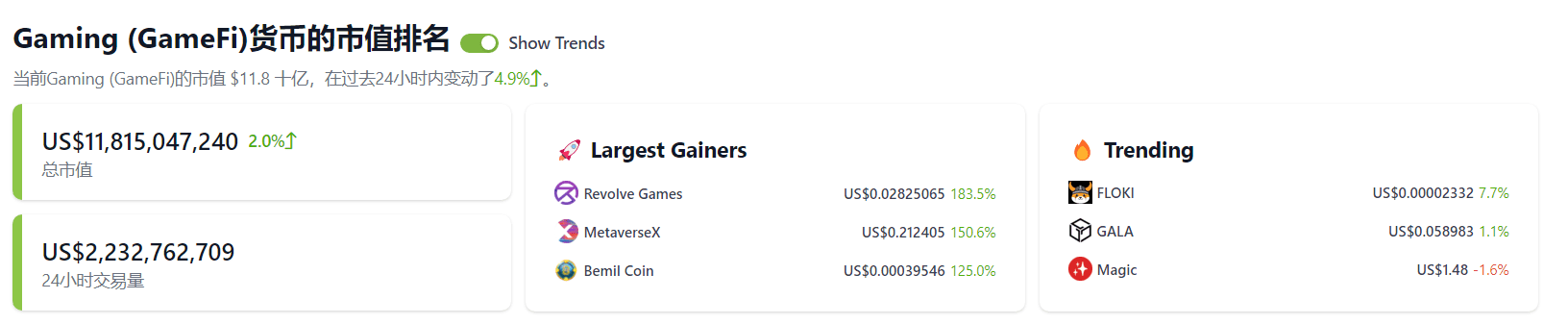
GameFi
GameFi literally means Game Finance, which is a fusion of games and finance, and is also a synonym for Web3 games. Before the term GameFi was born, Web3 games were usually called blockchain games, or simply chain games.
 CryptoKitties is the first widely known blockchain game. It is a virtual cat-raising game, and each cat is an independent NFT. There are a total of 50,000 cats in the first generation, and each cat has different attributes. After players purchase cat NFTs, they can start playing the game of breeding kittens. Some genetic attributes of the kittens born will be inherited from the previous generation, while some genes are randomly generated. The cats born are essentially new NFTs that can be sold for cash. If the new cats generated have rare genetic attributes, they can also be sold for a good price. As of the date of writing (end of January 2023), 2,021,774 cats have been generated, and there are 136,283 wallet addresses holding them.
CryptoKitties is the first widely known blockchain game. It is a virtual cat-raising game, and each cat is an independent NFT. There are a total of 50,000 cats in the first generation, and each cat has different attributes. After players purchase cat NFTs, they can start playing the game of breeding kittens. Some genetic attributes of the kittens born will be inherited from the previous generation, while some genes are randomly generated. The cats born are essentially new NFTs that can be sold for cash. If the new cats generated have rare genetic attributes, they can also be sold for a good price. As of the date of writing (end of January 2023), 2,021,774 cats have been generated, and there are 136,283 wallet addresses holding them.
Following CryptoKitties, more and more cultivation games have emerged, such as Crypto Dongle, Crypto Rabbit, Crypto Frog, etc. Breaking this situation is a game called Fomo3D, which is an open, transparent, and decentralized gambling fund game. The rules of the game are also simple. Users participate in the game by paying ETH to purchase Key. The ETH paid by users will be allocated to the prize pool, dividend pool, airdrop pool, official pool, etc. If you have a Key, you can get continuous dividends. The more Keys you have, the more dividends you will get. And there is a countdown (24 hours) for each round of the game. At the end of the countdown, the last player to buy a Key can get most of the ETH in the prize pool. But every time a user buys a Key, the remaining countdown time will increase by 30 seconds. The first round of the game lasted for a long time, and in the end someone used technical means to win the prize pool. After Fomo3D became popular, various optimized and upgraded versions of similar games continued to appear, but it turned out that this type of game still cannot last.
After that, the game that set off the market again was Axie Infinity, which is called "Axie" in China (homonymous with Axie). This is a game that combines the gameplay of Pokémon and CryptoKitties. The Axies in the game can be upgraded, bred, fought, and traded. Unlike games such as CryptoKitties, Axie Infinity's economic system also introduces SLP and AXS tokens. Players can win SLP tokens through battles, and new Axies can be bred by consuming SLP and AXS. The SLP tokens won and the bred Axies can be sold on the market to earn income.
However, Axie Infinity was actually launched in 2018, but it did not become popular until 2021. The main reason for its popularity is that its Play-To-Earn model has been promoted, that is, the feature of earning money while playing has spread virally. Its way to make money is mainly to first invest in the purchase of Axies, then earn SLP tokens and breed new Axies by playing games, and then sell SLP tokens and Axies for ETH or stablecoins, and finally exchange ETH or stablecoins for fiat currency. This money-making model first became popular in the Philippines. At that time, the outbreak of the new crown epidemic caused many local people in the Philippines to fall into the predicament of no income, and the feature of Axie Infinity to earn money while playing gave these people hope. Moreover, this money-making model has also attracted many gold-making studios, and has gradually expanded from the Philippines to India, Indonesia, Brazil, China, etc. As of the date of writing, the number of daily active users has reached 2.8 million.
Now, the earn-while-playing model has almost become a standard feature of Web3 games.
Other well-known games include Decentraland, The Sandbox, Illuvium, Star Atlas, Alien Worlds, etc. I won’t go into detail about these, and you can search and learn more about them if you are interested.
SocialFi
SocialFi, as the name implies, is Social Finance, an organic combination of social and finance in the Web3 field. In fact, it is decentralized social networking, a concept that has only become popular in the past two years. At present, there are relatively few well-known projects in this field, and the current leader is Lens Protocol.
Lens Protocol was developed by the Aave team and launched in May 2022. It is not an independent social application, nor a complete social product with a front-end, but a social graph platform that provides a series of modular components, and specific application products can be built using these components. Therefore, the definition of Lens is actually the infrastructure of Web3 social applications. At the beginning of its launch, it already had more than 50 ecological projects, the more popular ones are Lenster, Lenstube, ORB, Phaver, re:meme, Lensport, Lensta, etc.

Lenster is a decentralized social media application that can be logged in by connecting a Web3 wallet and using Lens. Logged-in users can post content on Lenster, similar to posting content on Weibo or Twitter, but with the option to charge a fee when posting content on Lenster. Users can also comment on other users' content, but hierarchical comments are not currently supported.
Lenstube is a decentralized video platform, which can be understood as a decentralized Youtube.
ORB is a decentralized professional social media application with an end-to-end on-chain reputation system. Specifically, ORB can create personal decentralized professional profiles and establish on-chain credibility by linking various NFTs and POAPs with user experience, education, skills, and projects, as well as explore job opportunities and apply for on-chain identities. It can also be used to share one's ideas on the chain, connect with Web3 people, and build communities. In addition, ORB also allows users to use fragmented time to acquire NFTs by learning Web3 knowledge, namely Learn-to-Earn.
Phaver is a Share-to-Earn social app for iOS and Android. Users can post content such as pictures, links, product applications, etc. Users can also browse all the content in Lens. Lens Profile After users connect their wallets, they can also post directly to Lens through Phaver.
re:meme is an on-chain meme generator that allows users to upload meme templates and choose whether to charge a fee. Others can then use an image editor to add text, drawings, and additional images. :meme can also be extended to media formats such as music, videos, and academic papers.
Lensport is a social NFT marketplace focused solely on the Lens protocol, where users can discover, publish and sell posts, as well as invest in supporting creators.
Lensta is a photo streaming application focused on the Lens protocol, which allows you to browse the latest, most popular and most collected posts on Lenster, Lensport, etc. with pictures in Lens.
Access Layer
The access layer is the top layer in the Web3 architecture and is also the entry layer directly facing end users.This layer mainly includes wallets, browsers, aggregators, etc. In addition, some Web2 social media platforms have also become the entrance to Web3.

Let’s first look at the wallet, which is also the main entry point. Currently, there are many types of wallets, including browser wallets, mobile wallets, hardware wallets, multi-signature wallets, MPC wallets, smart contract wallets, etc.
Browser wallets are crypto wallets used through web browsers. They are the most widely used wallets by most users. The most commonly used ones are MetaMask, Coinbase Wallet, WalletConnect, etc. MetaMask is one of the most widely supported wallets. It supports all EVM chains and has become the standard for all DApps. Currently supported browsers include Chrome, Brave, Firefox, and Edge, which exist as browser plug-ins. Coinbase Wallet, as the name suggests, is a wallet issued by the exchange Coinbase. After its launch in November 2021, it has developed rapidly and has become a rival to MetaMask, but the browser only supports Chrome. WalletConnect is special. It is not a specific wallet application, but an open source protocol that connects DApps and wallets. The most commonly used one is to connect to mobile wallets. When you choose to connect to WalletConnect on the DApp on the browser, a QR code will be displayed. Scanning this QR code with your mobile wallet can authorize your mobile wallet to connect to the DApp on the browser. Moreover, WalletConnect supports all blockchains, not just EVM chains, but also supports access to all wallets. In addition, unlike MetaMask and Coinbase Wallet, which require browser plug-ins to be installed, WalletConnect does not require browser plug-ins to be installed, so it can support all browsers, such as Safari, while MetaMask and Coinbase Wallet do not support Safari. Therefore, WalletConnect has become the most popular wallet and the standard for all DApp access wallets.
Mobile wallets, that is, mobile digital asset wallets, are supported by many wallets. MetaMask and Coinbase Wallet also have mobile wallet apps. In addition, other well-known mobile wallets include TokenPocket, BitKeep, Rainbow, imToken, Crypto.com, etc. Most popular mobile wallets support multiple chains, including EVM chains and Non-EVM chains. For example, TokenPocket currently supports Bitcoin, Ethereum, BSC, TRON, Polygon, Arbitrum, Avalanche, Solana, Cosmos, Polkadot, Aptos, etc.
Hardware wallets store the private keys of digital assets in secure hardware devices that are isolated from the Internet and can be plug-and-play via USB. The most widely used hardware wallets are Ledger and Trezor. Ledger currently has three different models of hardware wallets: Ledger Stax, Ledger Nano X, and Ledger Nano S Plus. Ledger Stax is a new model launched in 2023 that supports touch screens, while the other two do not. Trezor has two models: Trezor Model T and Trezor Model One. Model T supports touch screens. In addition to Ledger and Trezor, other hardware wallets on the market include SafePal, OneKey, imKey, KeepKey, ColdLar, etc.
As the name implies, a multi-signature wallet is one that requires multiple signatures to execute operations. The most well-known multi-signature wallet is Gnosis Safe, which is essentially a set of on-chain smart contracts. The most commonly used is the 2/3 signature, which means that a total of three users jointly manage the wallet. Each time an operation is executed, the signatures of at least two of the three people are required to trigger the on-chain execution.
MPC stands for Multi-Party Computation. MPC wallet is also called multi-party computing wallet. It is a new generation of wallet type. It implements complex verification methods such as multi-signature and cross-chain off-chain by performing multi-party computation on private keys. In simple terms, it is to split the private key into multiple shards, and then multiple parties store and manage each shard separately. When signing, multiple parties will reassemble the shards into a complete private key. MPC wallet is very similar to multi-signature, and can also implement 2/3 signature. The difference is that multi-signature wallet implements signature verification at the smart contract level, while MPC wallet is implemented through off-chain calculation. At present, there are not many MPC wallet services, mainly ZenGo, Safeheron, Fordefi, OpenBlock, web3auth, etc.
A smart contract wallet is a wallet that uses a smart contract account as an address. The multi-signature wallet Gnosis Safe also belongs to a smart contract wallet. In the past one or two years, the latest attempt at smart contract wallets is a new generation of wallets that combines "Account Abstraction". Account abstraction is mainly to separate the signer from the account. The wallet address is no longer strongly bound to the only private key. It can realize the replacement of the signer, multi-signature, and signature algorithm. In addition to Gnosis Safe, there are also UniPass, Argent, Blocto, etc. in this field.
That’s all we have to say about wallets for now. Let’s move on to browsers. Many DApps still only provide a web version of the front end, so the browser has become an important access point. However, not all browsers support wallet extensions, so not all browsers can be a good Web3 entry point. The most commonly used browser is Chrome, and all browser wallets will develop Chrome wallet plug-ins. Safari is rarely used as a Web3 DApp entry point because, except for WalletConnect, no other browser wallet can support it. Another browser worth introducing is Brave, which is a browser with a built-in wallet called Brave Wallet.

Some aggregators are also access points to Web3, such as DappRadar, which collects various DApps, and users can browse and connect to these DApps through it. There are also aggregators such as Zapper, DeBank, and Zerion, which can help users track all their assets and operation records in various Web3 applications.
Finally, Web3 social media platforms such as Twitter and Reddit have gradually become access portals to Web3 because they gather many Web3 communities.
Note: The market is risky, so be cautious when investing. This article does not constitute investment advice, and users should consider whether any opinions, views or conclusions in this article are suitable for their specific circumstances. Invest at your own risk.