Excellent software and practical tutorials
Color blindness and color weakness detection
Color blindness is a congenital color vision disorder. There are many types of color vision disorders, the most common of which is red-green color blindness. According to the theory of three primary colors, any color in the visible spectrum can be composed of red, green and blue. People who can recognize the three primary colors are normal people, and those who cannot recognize the three primary colors are called total color blindness. People with reduced ability to recognize any color are called color deficient, mainly red-green color deficient, and blue-yellow color deficient. People who cannot recognize one primary color are called dichromats, mainly red-green color blindness and green-green color blindness.
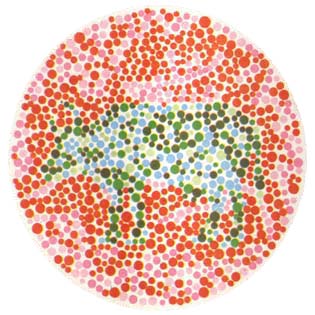
Here are someColor blindness test chart, I hope everyone can check it out by themselves. If you are unfortunately tested as color blind or color weak, I hope you will not be sad. It is determined by genetics. The following can further determine what kind of color weakness you have. Color discrimination ability judgment.
Patients who lack color vision or have incomplete color vision are called color blindness, and low color discrimination ability is called color weakness. The color blindness rate of Chinese men: 4.71+-0.074%; the color blindness rate of women: 0.67+-0.036%; the frequency of color blindness gene carriers: 8.98%, mostly caused by genetics. Want to know if you are color blind (color weak)? Here are some representative color blindness test pictures. Try to read all the pictures to see if the final test results are the same. If the test is color weakness, then it will not actually have any impact on your daily life. You will only find that you have color vision abnormalities when you look at some pictures with high color accuracy requirements.





What is color blindness?
Color blindness is a congenital color vision disorder, which refers to the lack or complete inability to distinguish colors. There are many types of color blindness, the most common of which is red-green color blindness. According to the theory of three primary colors, any color in the visible spectrum can be composed of red, green and blue. People who can recognize the three primary colors are normal, and those who cannot recognize the three primary colors are called total color blindness. People with reduced ability to recognize any color are called color weak, mainly red-green color weak, and blue-yellow color weak. If one of the primary colors cannot be recognized, it is called dichromatism, mainly red-green color blindness and green-green color blindness.
Color blindness refers to the lack of or complete inability to distinguish colors. Color blindness usually refers to red and green color blindness. Faced with a colorful world, how do people perceive it? It turns out that there is a kind of photoreceptor cell on the human retina - cone cells, which have three kinds of photosensitive pigments: red, green, and blue. Each photosensitive pigment is mainly excited by one primary color of light, and reacts to the other two primary colors to varying degrees. If a certain pigment is lacking, it will cause a sensory impairment to this color, which manifests as color blindness or color weakness (weak color discrimination).
The difference between color blindness and color weakness
Lack of color vision or incomplete color vision is called color blindness, and low color discrimination ability is called color weakness. Color blindness can be divided into total color blindness and partial color blindness. Total color blindness is extremely rare, and it is manifested as only being able to distinguish light and dark, and lacking color vision; partial color blindness is mostly red-green color blindness or blue-blue color blindness. Red-green color blindness is manifested as only being able to sense red or green, that is, being unable to distinguish red and green, which may be caused by the lack of red-sensitive cones or green-sensitive cones. Blue-blue color blindness is rare, and it is manifested as being dominant in the sense of green, yellow, and red, similar to blue weakness, and is related to the lack or scarcity of blue-sensitive cones. Color blindness can be congenital or acquired. Congenital color blindness is hereditary, and acquired color blindness can be improved by eliminating the cause or supplementing nutrition, such as increasing protein or vitamins A and B. In addition to congenital color blindness, color weakness often occurs in the acquired, which is caused by defects in color perception caused by poor health. It is manifested as a low ability to distinguish red, green, and blue. Acquired color weakness can be improved by eliminating the cause or supplementing nutrition.
Each photosensitive pigment is mainly excited by one primary color of light, and reacts to the other two primary colors to varying degrees. If a certain pigment is lacking, it will cause a sensory impairment to this color, manifesting as color blindness or color weakness (weak color discrimination). There are many different types of color blindness. Those who only lack the ability to distinguish one primary color are called monochromatic blindness. For example, red blindness, also known as first color blindness, is more common; green blindness, called second color blindness, is less common than first color blindness; blue blindness, also known as third color blindness, is relatively rare. If a person lacks the ability to distinguish two colors, it is called total color blindness, which is relatively rare. Color blindness is mostly caused by congenital inheritance, and a few are caused by disorders of the visual pathway conduction system. It is generally transmitted in females and manifested in males.
In theory, people with total color blindness should only see black and white, but this is not the case. Interestingly, people with red color blindness can still distinguish red traffic lights, and people with green color blindness can also distinguish green traffic lights. Why is this? This is because people with monochromatic blindness can distinguish the three primary colors, but cannot distinguish compound colors such as orange and light yellow.
Symptoms of color blindness
There are many different types of color blindness. Those who can only lack the ability to distinguish one primary color are called monochromatic blindness. For example, red color blindness, also known as primary color blindness, is more common; green color blindness, called secondary color blindness, is less common than primary color blindness; blue color blindness, also known as tertiary color blindness, is relatively rare. If a person can't distinguish two colors, it is called total color blindness, which is relatively rare. Color blindness is mostly caused by congenital inheritance, and a few are caused by visual pathway conduction system disorders. It is usually transmitted in women and manifested in men.
In theory, people with total color blindness should only see black and white, but this is not the case. Interestingly, people with red color blindness can still distinguish red traffic lights, and people with green color blindness can also distinguish green traffic lights. Why is this? This is because people with monochromatic blindness can distinguish the three primary colors, but cannot distinguish compound colors such as orange and light yellow.
Congenital color vision disorder is usually called color blindness, which is the inability to distinguish various colors or certain colors in the natural spectrum. Poor color discrimination ability is called color weakness, and the boundary between it and color blindness is generally not easy to strictly distinguish, but the severity is different. Color blindness is divided into total color blindness and partial color blindness (red blindness, green blindness, blue-yellow color blindness, etc.). Color weakness includes total color weakness and partial color weakness (red blindness, green blindness, blue-yellow color blindness, etc.).
Color blindness is divided into total color blindness and partial color blindness (red blindness, green blindness, blue-yellow color blindness, etc.), and color weakness includes total color weakness and partial color weakness (red blindness, green blindness, blue-yellow color weakness, etc.).
1. Total color blindness
It is a complete cone cell dysfunction, which is the exact opposite of night blindness (rod cell dysfunction). Patients prefer darkness and are afraid of light, which manifests as day blindness. The colorful world is gray in their eyes, just like watching a black and white TV, with only light and dark but no color difference. Moreover, red appears dark and blue appears bright. In addition, there are symptoms such as poor vision, amblyopia, central scotoma, and pendulum nystagmus. It is the most serious type of color vision disorder and patients are rare.
2. Red-color blindness
Also known as the first color blindness, patients are mainly unable to distinguish red, and cannot distinguish red from dark green, blue from purple-red, and purple. They often see green as yellow, purple as blue, and mix green and blue as white. Once a mature and steady middle-aged man bought a gray wool sweater, but was laughed at after he put it on. It turned out that he was a red-color blind patient who mistook red for gray. There was also a report in the early years that a red-color blind patient worked as a train driver and caused a train collision because he read the wrong signal.
3. Deuteranopia
Also known as the second color blindness, patients cannot distinguish between light green and dark red, purple and cyan, purple and gray, and see green as gray or dark black. In an art training class, there was a child who was very good at drawing. He always painted the sun green, and the treetops and grass brown. It turned out that he was a green-color blind patient. Clinically, red-green color blindness and green-color blindness are collectively referred to as red-green color blindness. Patients with this disease are more common. The color blindness we usually refer to is generally red-green color blindness.
4. Blue-yellow color blindness
Also known as the third color blindness, patients confuse blue and yellow, but can distinguish red and green. It is relatively rare.
5. Full color weak
Also known as red-green-blue-yellow color weakness, the color vision disorder is less severe than total color blindness. There is no abnormality in vision and no other complications of total color blindness. Objects can be distinguished when they are dark and bright in color; if the color is light and unsaturated, it is difficult to distinguish, and patients are rare.
6. Partial color weakness
There are red-green color weakness (first color weakness), green-green color weakness (second color weakness) and blue-yellow color weakness (third color weakness), among which red-green color weakness is more common. Patients have poor sensitivity to red and green. When the lighting is poor, their color discrimination ability is close to red-green color blindness; but when the color of the material is dark, bright and the lighting is good, their color discrimination ability is close to normal.