Excellent software and practical tutorials
Install Redis on Linux to make PHP access faster
Install Redis on Linux , what should I do if the PHP website access speed is slow? Now many people use WordPress to build websites. WordPress is a large blog program developed based on PHP. How to improve the access speed of WordPress websites? Here you need to install the server-side cache tool Redis. The following is a detailed explanation of what Redis is and how to install Redis in Linux
PHP caching tool Redis
Redis is the most popularPHP Cache ToolOne. In the early days of Web application development, relational databases received widespread attention and application because Web sites at that time had low access and concurrency and few interactions. Later, with the increase in traffic, Web sites using relational databases began to encounter some performance bottlenecks, and the source of the bottleneck was generally the disk I/O. With the further development of Internet technology, various types of applications have emerged in an endless stream, which has led to more performance requirements in today's era of cloud computing and big data, mainly reflected in the following four aspects:
- Low latency read and write speed: Fast application response can greatly improve user satisfaction
- Supporting massive amounts of data and traffic: For large applications such as search, it is necessary to use PB-level data and be able to handle millions of traffic.
- Management of large-scale clusters: System administrators hope that distributed applications can be deployed and managed more easily.
- Consideration of huge operating costs: IT departments hope to significantly reduce hardware costs, software costs, and labor costs.
In order to overcome this problem, NoSQL came into being. It has the advantages of high performance, strong scalability, and high availability, and is favored by a wide range of developers and warehouse managers.
What is Redis
Redis is one of the most popular NoSQL databases. It is an open source, memory-based, and optionally persistent key-value pair storage database written in ANSI C. It contains multiple data structures and supports networks. It has the following features:
- Based on memory operation, high performance
- Supports distribution and can be expanded infinitely in theory
- Key-value storage system
- Open source written in ANSI C, compliant with BSD protocol, supports network, can be based on memory or persistent log type, Key-Value database, and provides API in multiple languages
Compared with other database types, Redis has the following characteristics:
- C/S communication model
- Single process single thread model
- Rich data types
- The operation is atomic
- persistence
- High concurrent read and write
- Support lua script
Which big companies are using Redis?
- github
- Stack Overflow
- Alibaba
- Baidu
- Meituan
- Sohu
What are the application scenarios of Redis?
Redis application scenarios include: caching systems ("hot" data: high-frequency reads, low-frequency writes), counters, message queue systems, rankings, social networks, and real-time systems.

Redis data types and main features
The data types provided by Redis are mainly divided into 5 built-in types and one custom type. These 5 built-in types include: String type, hash type, list type, set type and sequential set type.
String type:
It is a binary-safe string, which means it can store not only strings, but also pictures, videos and other types, with a maximum length of 512M.
For each data type, Redis provides a variety of operation commands, such as:
- GET/MGET
- SET/SETEX/MSET/MSETNX
- INCR/DECR
- GETSET
- DEL
Hash Type:
This type is a map consisting of fields and associated values, where both fields and values are of string type.
The Hash operation commands are as follows:
- HGET/HMGET/HGETALL
- HSET/HMSET/HSETNX
- HEXISTS/HLEN
- HKEYS/HDEL
- HVALS
List Type:
This type is a collection of string elements sorted in insertion order, implemented based on a doubly linked list.
The List operation commands are as follows:
- LPUSH/LPUSHX/LPOP/RPUSH/RPUSHX/RPOP/LINSERT/LSET
- LINDEX/LRANGE
- LLEN/LTRIM
Collection Type:
The Set type is an unordered collection. The biggest difference between it and the List type is that the elements in the set have no order and the elements are unique.
The underlying layer of the Set type is implemented through a hash table, and its operation commands are:
- SADD/SPOP/SMOVE/SCARD
- SINTER/SDIFF/SDIFFSTORE/SUNION
The Set type is mainly used in certain scenarios, such as social scenarios. Through intersection, union, and difference operations, the Set type can be used to easily find social relationships such as common friends, common concerns, and common preferences.
Sequential collection types:
ZSet is an ordered set type. Each element is associated with a double-type score weight, which is used to sort the members in the set from small to large. Like the Set type, its underlying structure is also implemented through a hash table.
ZSet Command:
- ZADD/ZPOP/ZMOVE/ZCARD/ZCOUNT
- ZINTER/ZDIFF/ZDIFFSTORE/ZUNION
Redis data structure
The data structure of Redis is shown in the following figure:
Some explanations about the above table:
- Compressed lists are one of the underlying implementations of list keys and hash keys. When a list key contains only a small number of list items, and each list item is either a small integer or a short string, Redis will use compressed lists as the underlying implementation of the list key.
- Integer sets are one of the underlying implementations of set keys. When a set contains only integer value elements and the number of elements in this set is small, Redis will use integer sets as the underlying implementation of set keys.
The following is an example of defining a Struct data structure:
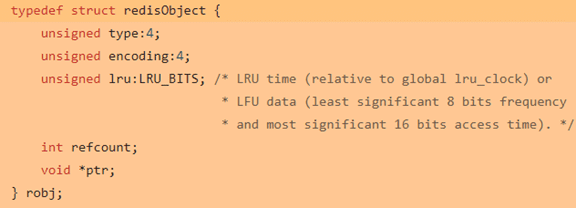
Simple Dynamic String SDS
Based on the defects of traditional strings in C language, Redis built an abstract type called simple dynamic string, referred to as SDS, with the following structure:
SDS runs through almost all data structures of Redis and is widely used.
Characteristics of SDS
Compared with C strings, SDS has the following characteristics:
- Constant complexity to get string length
In Redis, the len attribute of the SDS string can be used to directly obtain the length of the saved string.
The complexity of obtaining the length of a string is directly reduced from O(N) of a C string to O(1).
- Reduce the number of memory reallocations caused when modifying strings
From the characteristics of C strings, we know that for a C string containing N characters, its underlying implementation is always an array of N+1 characters long (with an additional null character at the end)
If the string needs to be modified at this time, the program needs to reallocate the memory of the C string array in advance (it may be expanded or released)
Memory reallocation means it is a time-consuming operation.
Redis cleverly uses SDS to avoid the defects of C strings. In SDS, the length of the buf array is not necessarily the number of characters in the string plus one. The buf array can contain unused bytes, which are recorded by the free attribute.
At the same time, SDS adoptedSpace pre-allocationThis strategy avoids the time-consuming memory reallocation operation every time the C string is modified, and reduces the memory reallocation from N times for every N modifications to a maximum of N times for N modifications.
The following is Redis's simple definition of SDS:
Redis feature 1: transactions
- Command serialization, executed in order
- Atomicity
- Three phases: Start transaction - Enqueue command - Execute transaction
- Command: MULTI/EXEC/DISCARD
Redis Feature 2: Pub/Sub
- Pub/sub is a messaging model
- Pub sends messages, Sub receives messages
- A Redis client can subscribe to any number of channels
- “fire and forgot”
- Command: Publish/Subscribe/Psubscribe/UnSub
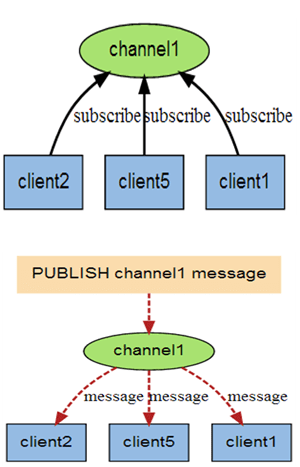
Redis feature 3: Stream
- What's New in Redis 5.0
- Waiting for consumption
- Consumer group (intra-group competition)
- Consumption history data
- FIFO
The above are the basic concepts of Redis. Next, we will introduce the "pitfalls" that you may encounter during the development process.
Redis FAQ: Breakdown
Concept: When Redis retrieves a key, because the key does not exist, a request must be made to the DB, which is called "Redis breakdown".
Causes of breakdown:
- First visit
- Malicious access to non-existent keys
- Key Expired
Reasonable workaround:
- When the server starts, write in advance
- Standardize key naming and intercept through middleware
- For some frequently accessed keys, set a reasonable TTL or never expire
Redis FAQ: Avalanche
Concept: When the Redis cache layer goes down for some reason, all requests will flow to the storage layer. High concurrent requests in a short period of time may cause the storage layer to hang up, which is called "Redis avalanche".
Reasonable workaround:
- Using Redis Cluster
- Current Limitation
Application practice of Redis in product development
For this reason, I am very happy to introduce to you that Jim, the architect of Grape City, will bring you an open class at 2019-11-27 14:00. In addition to explaining the basics of Redis, Jim will also demonstrate the problems and solutions encountered by his project team when using Redis. For students who are new to Redis, it is more meaningful and valuable for reference and learning. Everyone is welcome to participate. The open class address is:https://live.vhall.com/661463644.
- The backend uses nodeJS
- Using Azure Redis Service
- Redis usage scenarios
- token cache, used for token verification
- IP Whitelist
Problems encountered
- "Network jitter" or Redis service abnormality causes Redis access timeout
- Redis client driver stability issue
- Connection pool "Broken connection" problem
- Redis reset problem caused by JS Promise
Let's take a brief look at the advanced knowledge of Redis.
Advanced Introduction to Redis Protocol
Redis client communication protocol: RESP (Redis Serialization Protocol), its characteristics are:
- Simple
- Fast parsing speed
- Good readability
Redis cluster internal communication protocol: RECP (Redis Cluster Protocol), its characteristics are:
- Each node has two TCP connections
- One is responsible for client-server communication (P: 6379)
- One is responsible for communication between nodes (P: 10000 + 6379)
Data types supported by the Redis protocol:
- Simple characters (first byte: "+")
"+OK\r\n"
- Error (first byte: "-")
"-error msg\r\n"
- Number (first byte: ":")
“:123\r\n”
- Batch characters (first byte: "$")
"&hello\r\nWhoa re you\r\n"
- Array (first byte: "*")
"*0\r\n"
"*-1\r\n"
In addition to Redis, what other NoSQL databases are there?
There are many NoSQL databases similar to Redis on the market. As shown in the figure below, in addition to Redis, there are MemCache, Cassadra and Mongo. Below, we will briefly introduce these databases:
Memcache:This is a database very similar to Redis, but its data types are not as rich as Redis. Memcache was developed by Brad Fitzpatrick of LiveJournal. As a distributed high-speed cache system, it is used by many websites to improve the access speed of websites. It has a significant effect on improving the access speed of some large websites that need to access the database frequently.
Apache Cassandra:(generally referred to as C* in the community) This is an open source distributed NoSQL database system. It was originally developed by Facebook to store simple format data such as inboxes.Google BigTable's data model andAmazon Dynamo's fully distributed architecture. Facebook made Cassandra open source in 2008. Due to its good scalability and performance, it is used by Apple, Comcast, Instagram, Spotify,eBay, Rackspace,NetflixIt has been adopted by well-known websites such as , and has become a popular distributed structured data storage solution.
MongoDB: It is a document-oriented NoSQL database based on distributed file storage, written in C++, and aims to provide scalable and high-performance data storage solutions for WEB applications. MongoDB is a product between relational databases and non-relational databases. It is the most feature-rich and relational database among non-relational databases. The data structure it supports is very loose, and is a BSON format similar to json.
Install Redis on Linux
The following uses the centos system as an example to install Redis and apply Redis in WordPress.
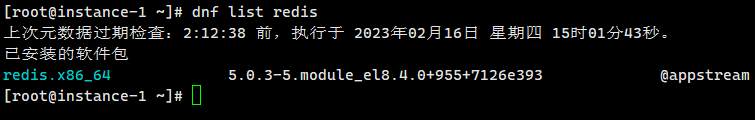
Install Redis using DNF
dnf install redis
Use the list command to check whether the installation is successful.
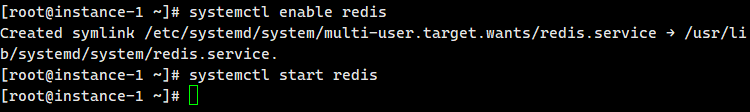
After installation, set the boot and start service
systemctl enable redis systemctl start redis
Use the command to check the running status of Redis.
systemctl status redis
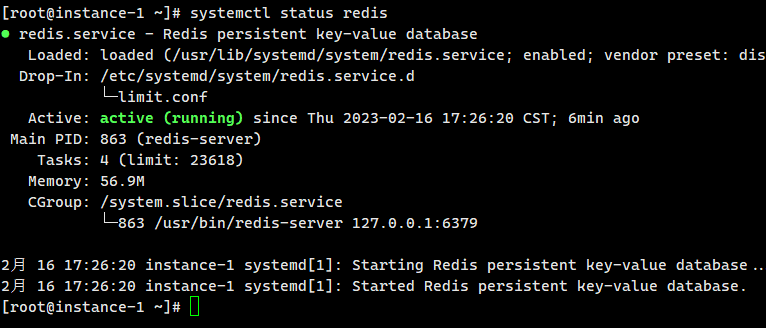 It is convenient and quick to install Redis using DNF. Redis is now installed. The Redis configuration file is located at: /etc/redis.conf
It is convenient and quick to install Redis using DNF. Redis is now installed. The Redis configuration file is located at: /etc/redis.conf
Install redis plugin in wordpress
Search for redis in the WordPress background plugin
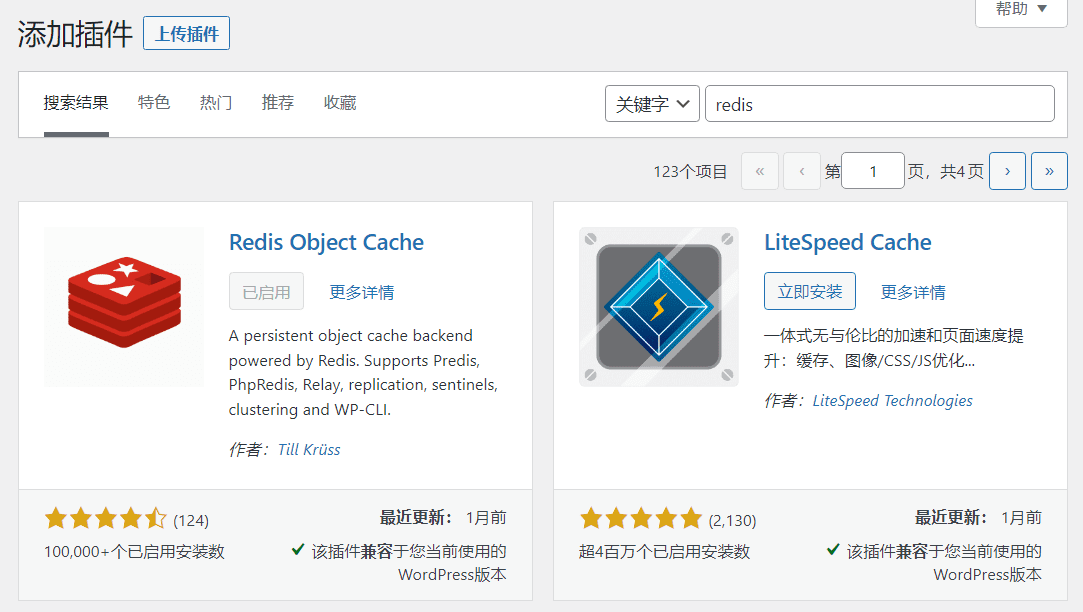
Installing Redis Object Cache
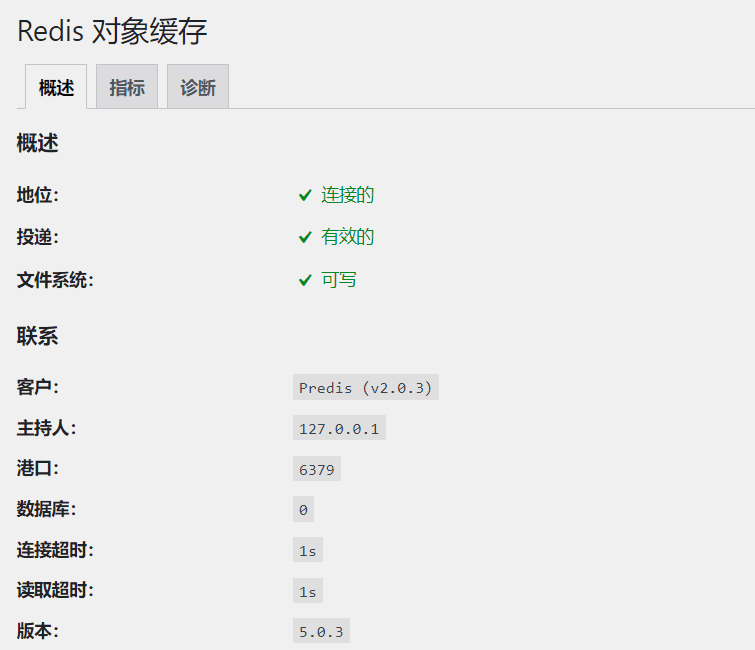
If you need the professional version of the plug-in, you need to install the PHP extension.












