Excellent software and practical tutorials
AlistAlist is a file list program that supports multiple storage, web browsing and WebDAV. It is an open source program for network disk file management driven by gin and Solidjs. Alist can not only mount local storage, but also various network disks, such as Alibaba Cloud, Baidu Cloud, 123, etc. Next, we will use the docker method to deploy Alist and mount the local directory.
The version we use is the Docker version that supports aria2, the URL is https://hub.docker.com/r/xhofe/alist-aria2
sudo docker run -d --restart=always -v /etc/alist:/opt/alist/data -p 5244:5244 -e PUID=0 -e PGID=0 -e UMASK=022 --name="alist" xhofe/alist-aria2:latest
will be completed automatically.
For the first use, query the default password:
sudo docker exec -it alist ./alist admin
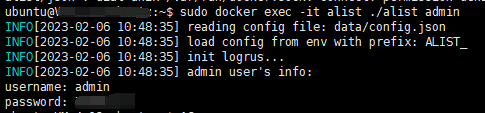
Log in with this administrator account: server ip:5244, click on the footer management, and then click on the left: storage, add, local storage. Among them, the mount path refers to the path displayed on the web page, and / is directly displayed in the root directory. The root folder path is where the file is actually stored on the server. It is worth noting that because we use the docker method, this path is actually in docker. If you want to access this file in the server, you need to enter docker first:
1. Get the ID of the alist container
sudo docker ps
2. Enter the container's command line
sudo docker exec -it 7dfc82a85888 /bin/bash
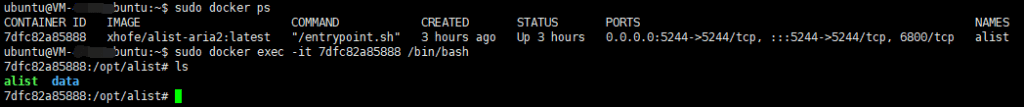
At this time, the root directory of the container corresponds to the root directory of the "root folder path". For example, I created a new folder named alist in the root directory of the container, which contains a test.txt file. I filled in the root folder path as "/alist" and the mount path as "/114514", then I will see the following in server ip:5244:
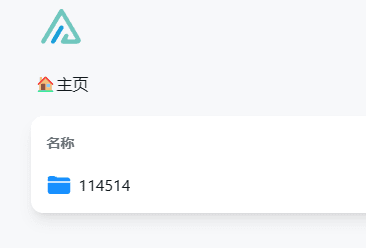
How to manage files in Docker containers
Although Docker containers are similar to virtual machines, there are still some differences when you want to transfer files between a physical machine and the system in the container.
If you only want to manage local files in the container system, then use docker exec This type of command goes directly into the container and can be managed using regular command lines.
But often there is a sudden need to copy files from an external physical machine to the container, or to copy files out of the container. The disadvantage of Docker is that it is troublesome to modify parameters once the container is created. It is obviously impossible to anticipate all subsequent needs and map all directories in advance when creating the container.
Fortunately, Docker itself provides corresponding file transfer commands, namely the copy and add instructions. These two instructions are similar in usage but have some differences.
The copy command, as its name implies, is a basic command that can be used to copy files between a container and an external physical machine. The command format can have multiple combinations depending on the target:
docker cp container ID or name: container directory physical machine directorydocker cp physical machine directory container ID or name: container directoryFor example, a mirror is created with a container ID of b2860e937844.
For example, if you want to copy the /home/lishuma directory of the physical machine to the /home directory of the container, run:
docker cp /home/lishuma b2860e937844:/home/After running, enter the container to view the corresponding directory, and you can see the corresponding lishuma directory:

If the trailing slash is removed from the previous command, it means copying the physical machine's /home/lishuma directory to the container's root directory, and renaming the copied directory to home.
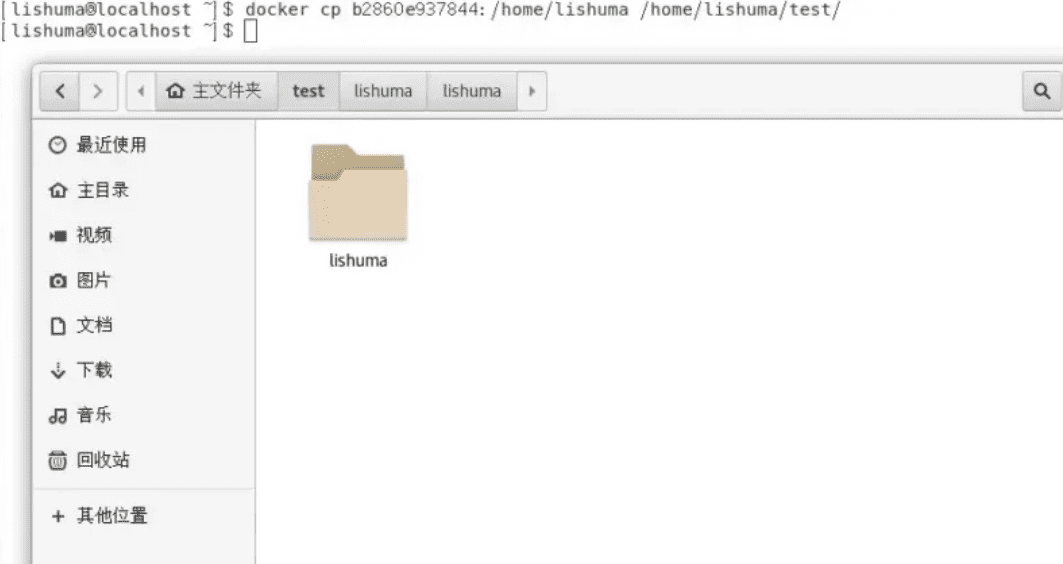
Then, conversely, if you want to copy the /home/lishuma directory of container b2860e937844 (which contains a test.zip file) to the /home/lishuma/test directory of the physical machine, the command format is:
docker cp container ID or name: container directory physical machine directoryrun:
docker cp b2860e937844:/home/lishuma /home/lishuma/test/After running, you can see that the required directory appears in the corresponding directory of the physical machine:
 External copy of container files
External copy of container filesAs above, if the last slash is removed from the command to copy the container outward, it means that the command will be renamed to test after being copied.
Note:
- If the source path is a file and the target path ends with /, Docker will treat the target path as a directory and copy the source file to that directory (if it does not exist, it will be created automatically).
- If the target file is an existing file, it will be overwritten by the source file and the file name will be the target file name.